Figure 2.
Structure-Guided Identification of a Motif that Predicts ICAM-1 Binding
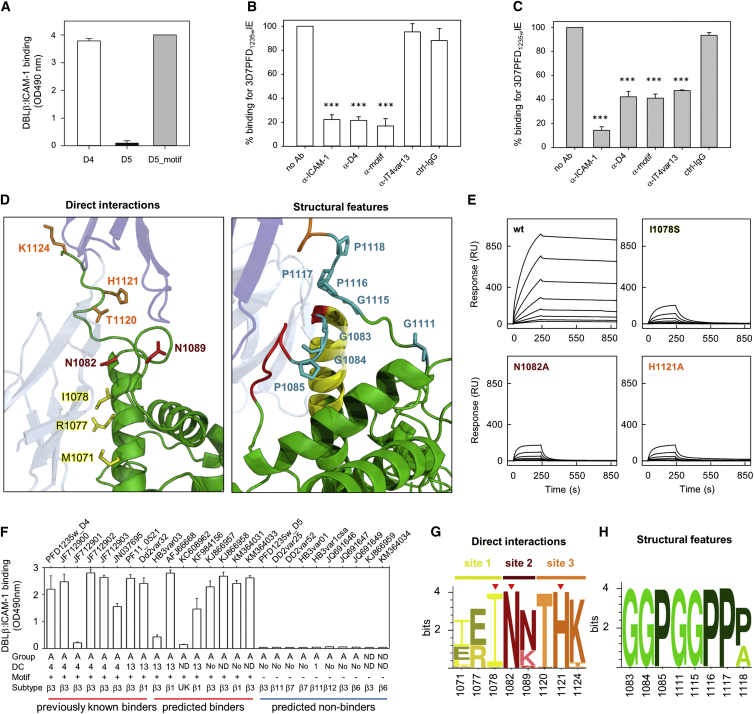
(A) ICAM-1 binding (ELISA OD 490 nm; ± SD) of recombinant 3D7 PFD1235w DBLβ3_D4, PFD1235w DBLβ3_D5, and a chimeric DBLβ3_D5 containing the ICAM-1-binding motif region of DBLβ3_D4 (D5_motif).
(B and C) Inhibition of 3D7 PFD1235W infected erythrocyte adhering to ICAM-1 under flow in the presence of anti-ICAM-1 Abs, affinity-purified anti-PFD1235w DBLβ3_D4 (anti-D4) IgG, anti-PFD1235w_motif IgG, anti-ITVAR13, and control IgG. IgG antibodies affinity purified from (B) rat anti-serum and (C) human serum. ± SD of a minimum of three independent experiments done in triplicate. Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. Asterisks indicate significance (p = 0.0004).
(D) The three sites within the PF11_0521 DBLβ3_D4-binding site, indicating residues that directly contact ICAM-1 (site 1, yellow; site 2, red; site 3, orange). Structural residues important for positioning of interacting residues are highlighted in teal.
(E) Surface plasmon resonance curves for injection of 2-fold dilution series of DBLβ wild-type and binding site mutants over ICAM-1D1D5.
(F) ICAM-1 binding (ELISA OD 490 nm; ± SD three replicates) of 26 recombinant group A DBLβ domains (4 DBLβ1, 14 DBLβ3, 2 DBLβ6, 2 DBLβ7, 2 DBLβ11, 1 DBLβ12, and 1 DBLβ unknown sub-class), confirming prediction of binding domains. “DC” indicates in which domain cassette the domain is found. “ND” indicates that the DC type is unknown as only the DBLβ sequence is available. “No” indicates that the domain is not part of a known DC. Presence of DC13 prior to DBLβ is indicated.
(G and H) Sequence logo showing conservation of (G) residues that contact ICAM-1 and (H) residues important for the unusual architecture of the ICAM-1-binding site, based on 145 DBLβ domains predicted to bind ICAM-1. Red triangles, residues critical for direct interaction with ICAM-1.
See also Figures S3–S5 and Tables S2, S3, and S4.