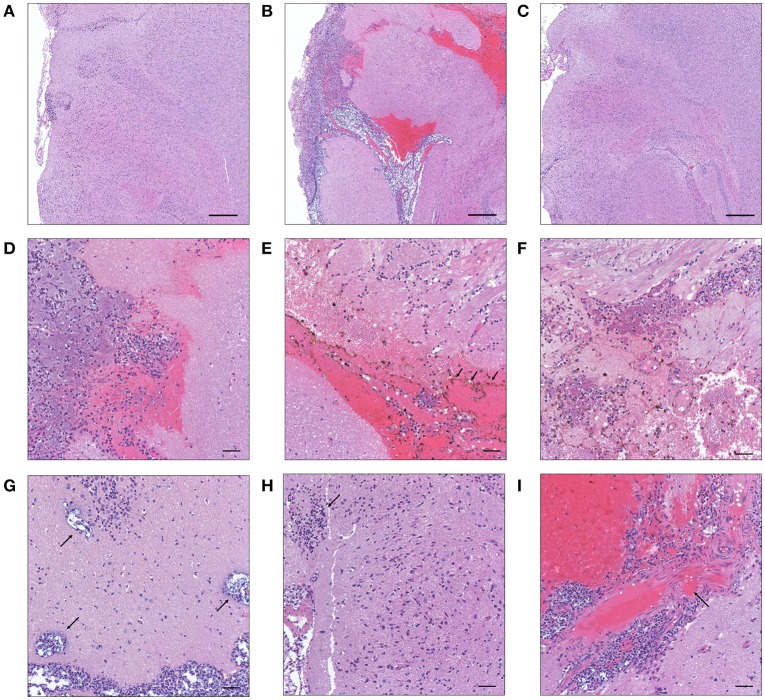
Figure 2.
Histopathological characteristics of K. pneumoniae 1084S-induced meningitis in adult BALB/c male mice. Representative images of brain sections retrieved from the control mice (A) and the mice at 7 days post-orogastric-inoculation with 1 × 109 CFU of K. pneumoniae 1084S (B) or with ΔClbA (C) are shown. In subarachnoid space of the 1084S-infected mice, numerous K. pneumoniae accumulated and neutrophils were recruited (D). Upon infection, typical characteristics of acute bacterial meningitis were developed, including superficial parenchymal damages, extensive focal hemorrhage with hemosiderin deposition (E), chronic hemorrhage lesions (F), edema in a perivascular region (G), aggregation of microglial cells (H), and micro-thrombosis (I). Scale bar in (A–I) is 500 and 50 μm, respectively.