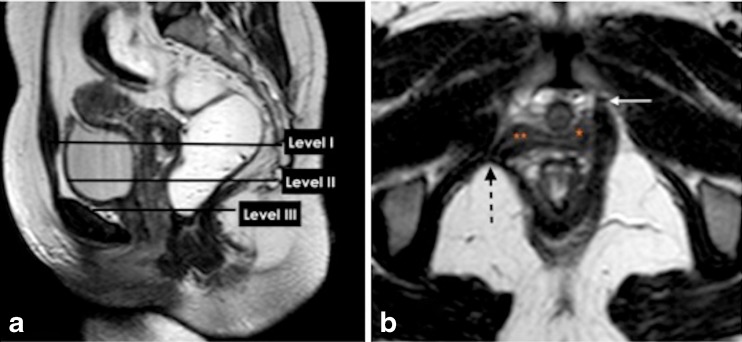
Fig. 5.
Functional three -part pelvic supporting system. a,b. Static T2W Turbo-Spin Echo (TSE) MR images in sagittal and axial plane. (a) Sagittal MR image illustrating the levels of the endopelvic fascia (paracolpium) that attaches the upper vagina to the pelvic walls, it is divided into three levels. Level I (suspension); the portion of the vagina adjacent to the cervix (the cephalic 2–3 cm of the vagina) functionally it provides the upper vaginal support. Level II (attachment); located in the mid portion of the vagina, it stretches the vagina transversely between bladder and rectum. The anterior vaginal wall provides urinary bladder support. The posterior vaginal wall and the endopelvic fascia (rectovaginal) form a restraining layer that prevents the rectum from protruding forward. (b) Axial T2W image shows detachment of the puborectalis muscle from its origin identified by discontinuity of its attachment to the pubic bone on the right side (dotted black arrow) (white arrow, normal bony attachment), (** loss of H-shaped vagina on the right side), (*; normal lateral vaginal attachment on the left side)