Figure 2.
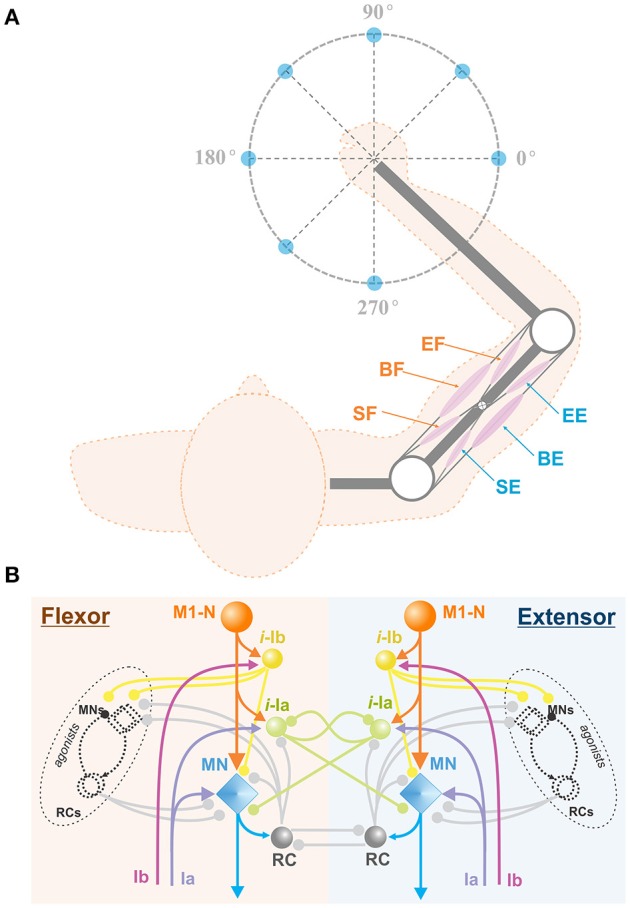
Arm model and spinal cord network. (A) Biomechanical arm model. The arm consists of 2 joints (white circles) at the shoulder and the elbow and 6 Hill-type muscles (pink ellipses), shoulder flexor (SF), bi-articular flexor (BF), elbow flexor (EF), shoulder extensor (SE), bi-articular extensor (BE), and elbow extensor (EE). This arm is designed to perform 2D reaching movements as described in Figure 1B. (B) Spinal cord network with afferent feedback. The spinal cord comprises interconnections of MNs, RCs, and interneurons. M1-Ns send motor command signals to MNs in the spinal cord, and MNs send muscle control signals to their corresponding arm muscles. The Ia and Ib inputs are the afferent feedback signals from the muscles. Interneurons take Ia and Ib inputs and modulate MN outputs. With RC connections, the spinal cord network mediates reflex responses. M1-N, Motor Cortex Neuron; i-la, la Interneuron; i-lb, lb Interneuron; RC, Renshaw Cell; MN, Motor Neuron; Ia, la afferent; Ib, lb afferent.
