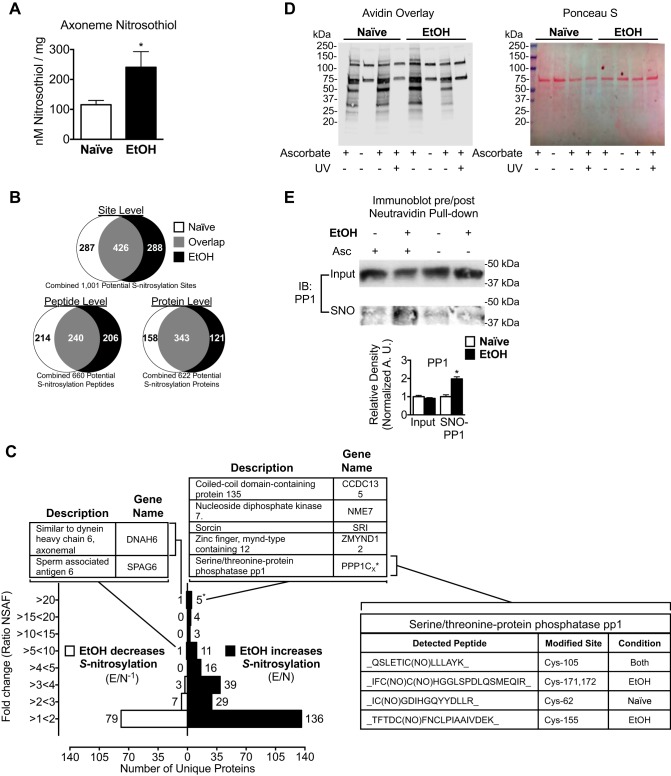
Fig. 1.
Alcohol exposure drives S-nitrosylation of key motility regulatory enzymes in bovine airway axonemes. A: axonemes extracted from bovine tracheae exposed to 100 mM alcohol (EtOH) contain more S-nitrosothiol (SNO) content compared with axonemes from alcohol-naive (Naive) bovine tracheae (240.6 ± 52.36 vs. 115.5 ± 14.36 nM/mg, n = 5). B: a total of 1,001 putative S-nitrosylated sites (cysteine residues) on 660 peptides corresponding to 622 SNO proteins were identified [Naive sample and EtOH (100 mM × 24 h)-treated sample]. There are 426 shared SNO sites, 240 shared SNO peptides, and 343 shared SNO proteins between the Naive and EtOH-treated samples. C: fold change increase or decrease in SNO in EtOH compared with Naive-identified peptides quantified by normalized spectral abundance factor (NSAF). The fold change in the S-nitrosylation increase was calculated by dividing EtOH by the Naive sample NSAF (E/N). The fold-change SNO decreased was calculated by performing the inverse (E/N−1) of values <1. Inset tables list the proteins (with gene names) identified with the indicated NSAF ratio, specific peptides detected, and cysteine residues modified from the bovine International Protein Index (IPI). *No peptides observed for protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) were isoform unique, and therefore, all peptides for PP1 were counted as 1 protein. Proteomic analyses are representative of replicate analyses performed on axonemes extracted from a single bovine tracheae that was cut in half, and each half was treated with media plus 100 mM alcohol for 24 h or media alone. D, left: axoneme proteins extracted from Naive (lanes 1–4) or EtOH (lanes 5–8)-treated bovine tracheae, labeled for total S-nitrosylation by the biotin switch technique (BST) in the presence (lanes 1, 3, 4, 5, 7, and 8) or absence (lanes 2 and 6) of ascorbate or prephotolyzed with UV light (lanes 4 and 8) as a control and assessed by avidin-horseradish peroxidase overlay. Right: Ponceau S staining as a loading control for the biotin switch assay. E: total and S-nitrosylated PP1 were then determined by NeutrAvidin pulldown and immunoblot (IB), demonstrating increased S-nitrosylation of PP1. Quantification of S-nitrosylation by densitometry is represented as the average ± SE of 3 independent experiments, 1 bovine trachea split into 2 parts for each experiment. Asc, ascorbate. *P ≤ 0.05.