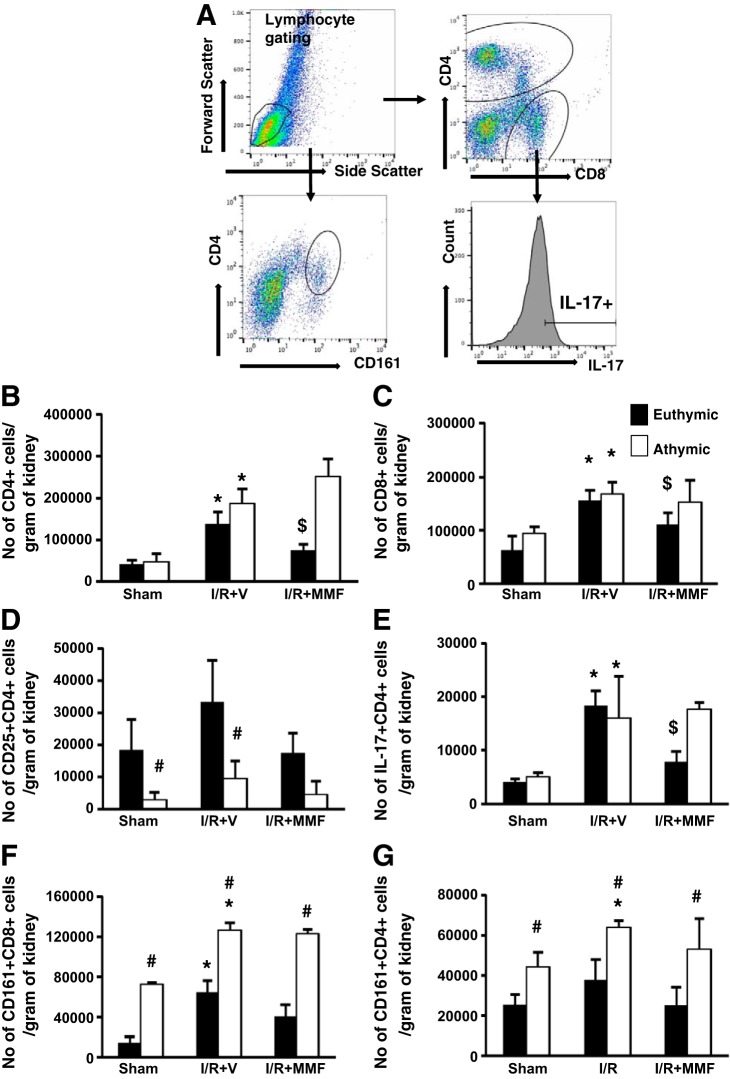
Fig. 3.
Phenotypic analysis of infiltrating mononuclear cells in immune-deficient athymic rats and immune-competent euthymic rats following I/R and exposure to high-salt diet. Lymphocytes were obtained from postischemic rats fed high-salt diet (4.0% NaCl) with or without MMF as labeled. A: gating strategy for FACS analysis. Lymphocytes were gated based on forward and side scatter plot. These were further gated based on the surface expression of CD4, CD8, and CD161. With the use of a histogram, CD4+ cells were further analyzed for expression of IL-17. B and C: no. of CD4+ (B) and CD8+ (C) cells isolated from kidneys. D: no. of activated T cells (CD4+CD25+) isolated from post-I/R or sham-operated rats fed high-salt diet with or without MMF. E–G: no. of CD4+IL-17+ (E), CD8+ natural killer T (NKT) cells (CD8+CD161+) (F), and CD4+NKT (CD4+CD161+) (G) cells isolated from athymic and euthymic rats treated with or without MMF. Data are means ± SE. P < 0.05, injury vs. sham group (*), MMF vs. vehicle ($), and athymic vs. euthymic (#) using ANOVA and Student-Neuman-Keuls post hoc test (n = 5–8 animals/group).