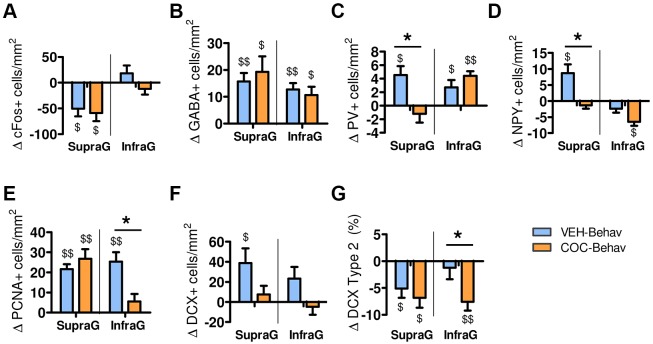
Fig. 7.
Behavior-induced modulation of plasticity in the DG is altered in cocaine-withdrawn mice. Change (Δ) in DG marker expression induced by behavior in VEH-Behav and COC-Behav mice compared with their respective control group (represented by zero in the graphs). The VEH-Behav mice showed notable behavior-induced changes, reducing basal c-Fos expression (A) but increasing GABAergic neuron populations (B-D) and adult hippocampal neurogenesis (E,F) in the DG after behavior training. However, the behavior-induced upregulation of PV and NPY was blunted in the supragranular layer of the COC-Behav mice (B,C). (G) In addition, the COC-Behav mice showed a blunted regulation of PCNA (E) and a reduced maturation of the young DCX+ neurons in the infragranular blade. Results are represented as mean±s.e.m. difference from the respective control group. Post hoc LSD test: *P<0.05 for VEH versus COC. One-sample Student's t-tests to compare means versus zero: $P<0.05, $$P<0.001 (this comparison indicates a significant change from the respective control group).