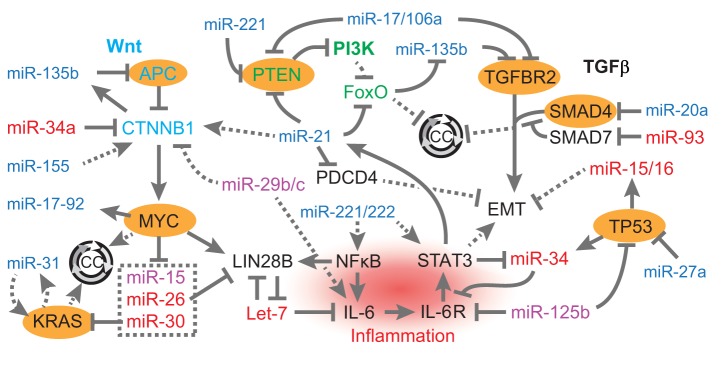
Fig. 2.
Genes frequently mutated in colorectal cancer and their relationships with miRNAs. Genes frequently mutated in CRC (highlighted in orange) regulate and are regulated by miRNAs. Oncogenic miRNAs are depicted in blue, tumor-suppressive miRNAs in red, and miRNAs with reported pleiotropic effects in purple. Direct relationships are shown with solid lines, while indirect relationships are illustrated with dotted lines. The Wnt pathway is augmented by miR-135b, miR-21 and miR-155, and inhibited by miR-34a, miR-29b/c. Downstream of Wnt, MYC transcriptionally activates the miR-17-92 locus, but represses expression of miR-15, miR-26 and miR-30. KRAS augments expression of miR-31. MYC and KRAS promote cell cycle progression (CC, circular arrows). In the PI3K pathway, which is negatively regulated by PTEN, miR-135b is augmented by PI3K inhibition of FoxO transcription factors (FOXO1 and FOXO3A), which represses cell cycle progression. MiR-221, miR-21 and miR-17/106 enhance activation of PI3K signaling by repressing negative regulators of this pathway. MiRNAs also modulate inflammatory pathways mediated by the transcription factors NFΚB and STAT3 by directly inhibiting IL-6 (via Let-7 miRNAs, which are inhibited by LIN28B) or the IL-6 receptor (via miR-34 and miR-125b). MiR-221/222 and miR-29b/c can also augment this pathway via indirect stimulatory effects on IL-6, NFΚB, and STAT3. The TGF-β pathway, which is important for repressing cellular proliferation and cell cycle progression is also antagonized by several miRNAs, including miR-17/106, miR-135b, and miR-20a through effects on TGFBR2 and SMAD4. The miRNA miR-93 can stimulate the TGF-β pathway by repressing the inhibitory SMAD7, although the effect of miR-93 is inhibitory of Wnt signaling through inhibition of SMAD7, which can augment nuclear accumulation of β-catenin. Lastly, several miRNAs have effects on EMT in CRC tumorigenesis, with miR-15/16 and miR-34 (which are transcriptionally activated by TP53) inhibiting this process, while miR-21 enhances EMT. References for the effects of these miRNAs can be found in Table 1 or in the main text. Official human gene symbols and full names: APC, adenomatous polyposis coli or WNT signaling pathway regulator; CTNNB1, β-catenin; MYC, v-myc avian myelocytomatosis viral oncogene homolog; KRAS, Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog or proto-oncogene and GTPase; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase (PIK3CA, PIK3CB, PIK3CD, PIK3CG); PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; FoxO, forkhead box O1 and O3a (FOXO1 and FOXO3A); PDCD4, programmed cell death 4 (neoplastic transformation inhibitor); LIN28B, lineage-28 homolog B; NFΚB, nuclear factor kappa B (NFKB1, NFKB2, REL, RELA, RELB); IL6, interleukin 6; IL6R, interleukin 6 receptor; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TGFBR2, transforming growth factor beta receptor 2; SMAD4, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog family member 4; SMAD7, mothers against decapentaplegic homolog family member 7; TP53, tumor protein p53.