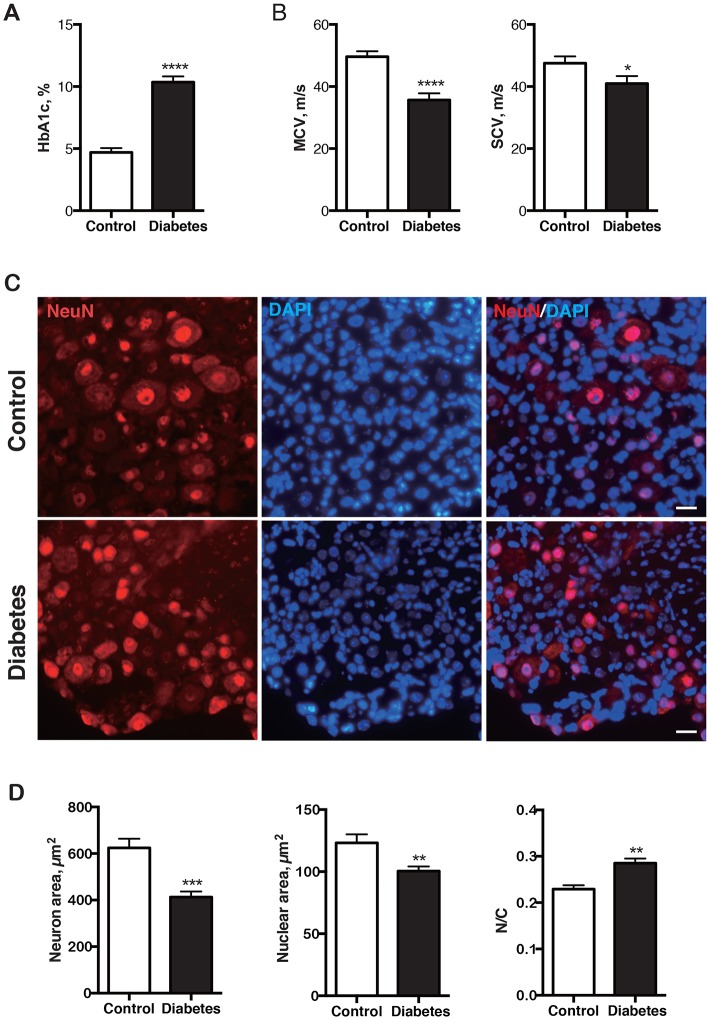
Fig. 1.
Nerve conduction slowing and DRG sensory neuron and nuclear atrophy in 16-week-old diabetic mice. (A) HbA1c was increased in diabetic mice (n=16) compared with nondiabetic controls (n=13). (B) Motor and sensory conduction velocities of diabetic mice were decreased compared with controls. Motor nerve: control, n=13; diabetes, n=11. Sensory nerve: control, n=13; diabetes, n=7. (C) Representative images of DRG sensory neurons stained with anti-NeuN antibody and DAPI in diabetic mice and controls. Scale bar: 20 μm. Diabetic sensory neurons were atrophic. (D) The average size of neuron and nucleus, and the nuclear-to-cytoplasmic (N/C) ratio of DRG neurons in diabetic mice (n=5) and controls (n=5). Both neuronal and nuclear size were smaller in diabetic mice than in controls, whereas N/C ratio was larger in diabetic mice. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001, unpaired one-tailed Student's t-test. Data represented as mean±s.e.m.