Fig. 1.
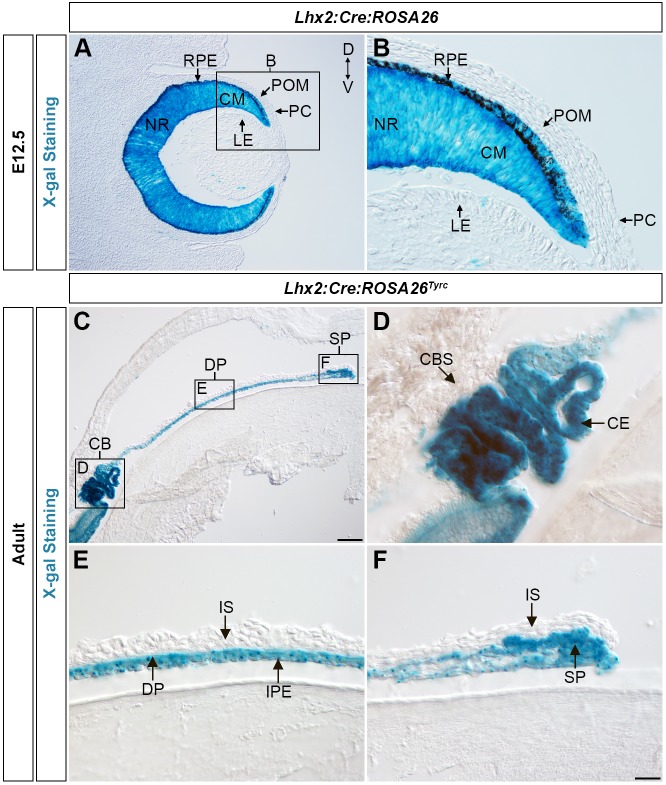
Lineage-tracing analysis of Cre recombinase expression in Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26R and Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26RTyrc mice. (A,B) X-gal staining in the developing eye of an Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26R mouse at E12.5 demonstrating β-gal activity in the NR, CM and RPE and confirming Cre-recombinase expression in these domains. No β-gal activity is observed in the LE, overlying POM or PC because of a lack of Cre recombinase expression in these regions. (C) X-gal staining of the anterior eye segment from an adult Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26RTyrc mouse demonstrating β-gal activity in the CB and iris. (D) X-gal staining of the CB from a Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26RTyrc mouse demonstrating β-gal activity in the CE. (E) X-gal staining of the medial iris from a Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26RTyrc mouse, demonstrating β-gal activity exclusively in the DP and IPE. (F) X-gal staining of the distal iris tip from a Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26RTyrc mouse demonstrating β-gal activity in the SP. No β-gal activity is observed in the IS because of the lack of Cre-recombinase expression in this tissue. All adult Lhx2-Cre:ROSA26RTyrc mice were analysed when older than 6 weeks. Scale bars: 100 µm (A,C), 25 µm (B,D-F). CB, ciliary body; CBS, ciliary body stroma; CE, ciliary epithelium; CM, ciliary margin; D, dorsal; DP, dilator pupillae; IPE, iris pigment epithelium; IS, iris stroma; LE, lens epithelium; NR, neural retina; PC, prospective corneal ectoderm; POM, periocular mesenchyme; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; SP, sphincter pupillae; V, ventral; X-gal, 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β-D-galactopyranoside.