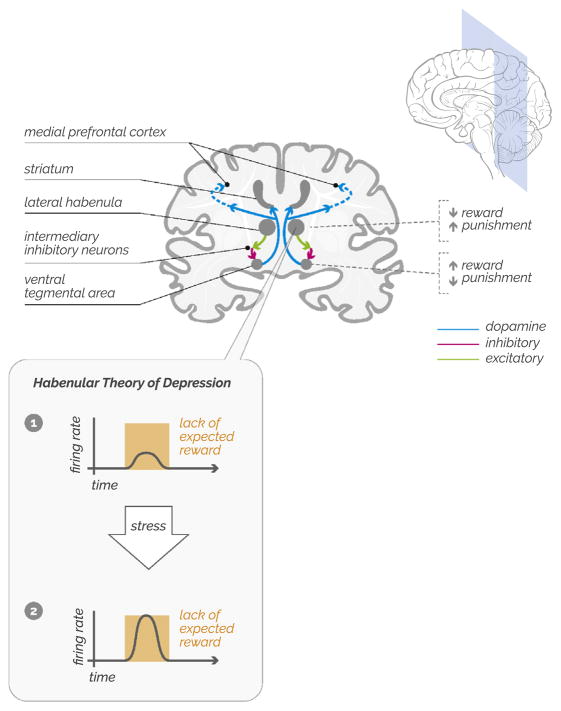
Figure 1.
Ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons convey learning signals related to unexpected rewards throughout the brain, with strong connections to the striatum and medial prefrontal cortex. Conversely, the lateral habenula signals the failure to receive an expected reward by sending excitatory inputs to the rostromedial tegmentum, which in turn suppresses ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons. The habenular model of depression is that chronic stress can lead to increased sensitivity of cells in the lateral habenula, thereby leading to more frequent signaling of disappointment or failure.