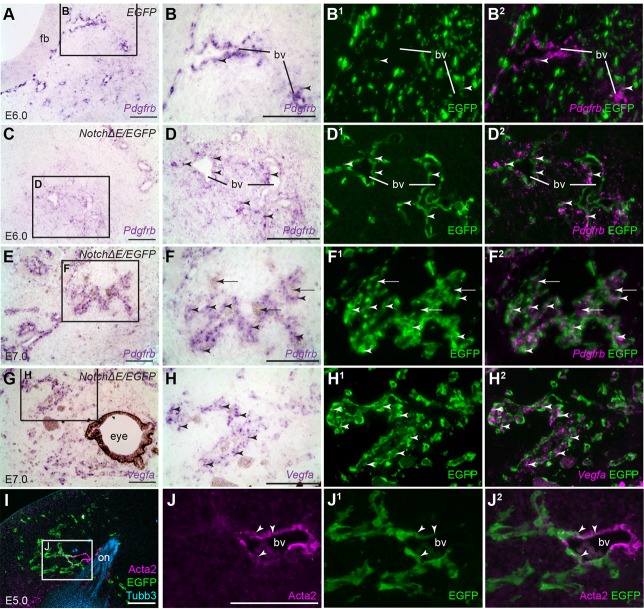
Fig. 2.
Constitutive Notch activation from E4 converts frontonasal mesenchyme cells to perivascular cells. Parasagittal sections of the frontonasal region from chicken embryos in which the cranial ectoderm had been targeted in ovo at E1 with EGFP alone (control) or NotchΔE/EGFP, using the Tol2 transposase/‘Tet-on’ electroporation system. Eggs were injected with doxycycline at E4. (A) A control EGFP-targeted embryo at E6. In situ hybridisation for Pdgfrb reveals perivascular cells in rings in the frontonasal mesenchyme and at the edge of the forebrain. (B) Higher-power view of boxed region in A, showing Pdgfrb-positive perivascular cells associated with a blood vessel near the forebrain. (B1,B2) Same section as B immunostained for EGFP, with Pdgfrb shown as a false-colour overlay in B2, reveals a fairly uniform distribution of EGFP-targeted cells in the mesenchyme and almost no co-localisation with Pdgfrb, apart from a few cells (arrowheads). (C-D2) A NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted embryo at E6. NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted cells are found in rings around the developing blood vessels and express Pdgfrb (arrowheads highlight examples), showing they are perivascular cells. (E-F2) A NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted embryo at E7. Blood vessels in the frontonasal mesenchyme (arrows indicate blood cells) are surrounded by NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted, Pdgfrb-positive perivascular cells (arrowheads). (G) In the same NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted embryo at E7, Vegfa is expressed in developing vasculature in the frontonasal mass. (H-H2) Higher-power view of the boxed region in G, revealing Vegfa-positive NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted cells (arrowheads). (I-J2) A NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted embryo at E5, with NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted cells in rings in the frontonasal mesenchyme. Immunostaining for alpha-smooth muscle actin (Acta2) reveals a few Acta2-positive NotchΔE/EGFP-targeted cells (arrowheads) associated with a large blood vessel near the olfactory nerve. bv, blood vessel; EGFP, enhanced GFP; fb, forebrain; on, olfactory nerve. Scale bars: 100 µm.