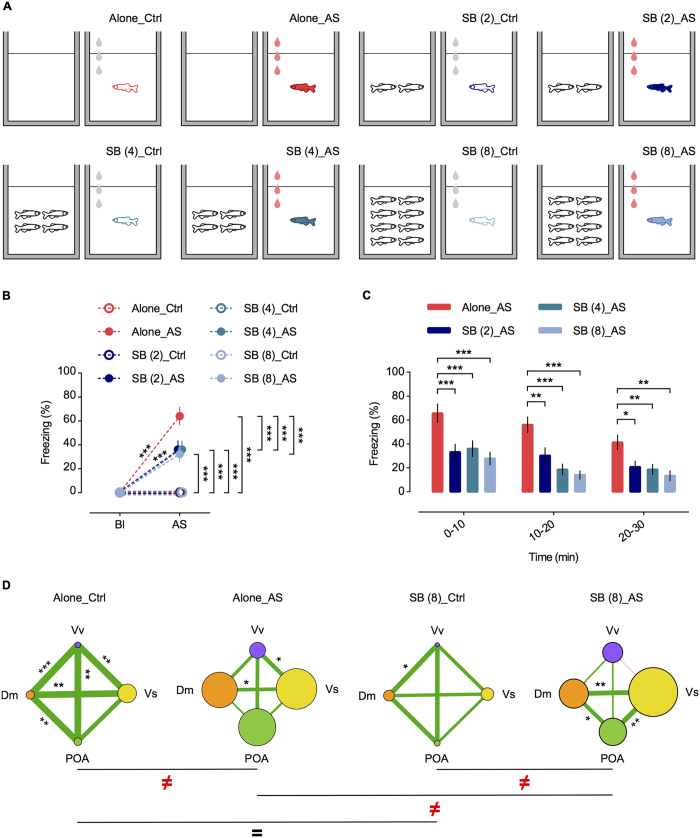
Figure 4. Experiment III.
(A) Schematic representation of the behavioural treatments. From left to right (top panel): Alone_Ctrl–alone focal fish (red outline) administered with water; Alone_AS–alone focal fish (red filling) administered with AS; SB (2)_Ctrl–focal fish (dark blue outline) administered with water and exposed to a shoal of 2 conspecifics; SB (2)_AS–focal fish (dark blue filling) administered with AS and exposed to a shoal of 2 conspecifics. From left to right (bottom panel): SB (4)_Ctrl–focal fish (sea blue outline) administered with water and exposed to a shoal of 4 conspecifics; SB (4)_AS–focal fish (sea blue filling) administered with AS and exposed to a shoal of 4 conspecifics; SB (8)_Ctrl–focal fish (light blue outline) administered with water and exposed to a shoal of 8 conspecifics; SB (8)_AS–focal fish (light blue filling) administered with AS and exposed to a shoal of 8 conspecifics. Grey and red drops represent water and AS administration, respectively. (B) Freezing % in baseline (Bl) vs. first 5 min after AS onset (AS). n = 20 per treatment. Mean ± SEM are shown. *p’ < 0.05; **p’ < 0.01 and ***p’ < 0.001. (C) Freezing % over the 30 min test in 10 min bins. n = 20 per treatment. Mean ± SEM are shown. *p’ < 0.05; **p’ < 0.01 and ***p’ < 0.001. (D) Brain networks as measured by c-fos mRNA expression for each treatment. Circle diameters represent the mean c-fos expression for each brain nuclei. Distinct (≠) and similar (=) co-activation patterns of c-fos mRNA expression between treatments are indicated. Lines linking brain nucleus represent the co-activation between them, as revealed by Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r), with line thicknesses proportional to r value and positive/negative correlations indicated by line colour (green and red, respectively); asterisks indicate significant correlations: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.