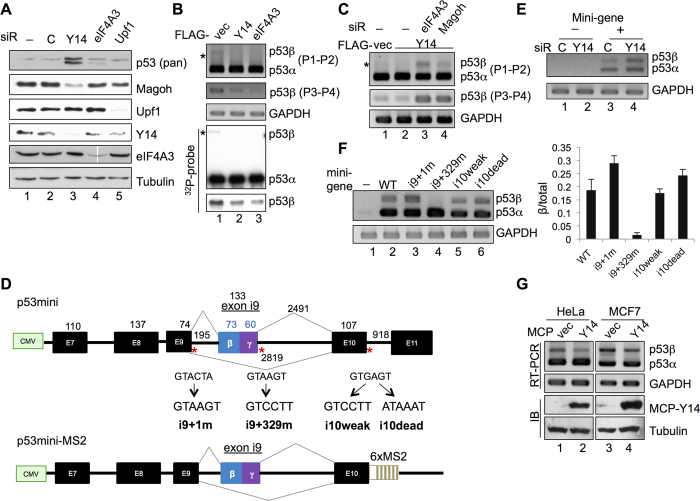
Figure 2. The EJC core prevents p53β expression.
(A) Immunoblotting of p53, Magoh, Upf1, Y14, eIF4A3, and α-tubulin in mock-transfected or siRNA-transfected HeLa cells. (B) RT-PCR of p53 using primers P1–P2 and P3-P4 in HeLa cells transfected with the empty or FLAG-Y14 or eIF4A3 expression vector. GAPDH served as the control. Bottom panels show Southern blotting of the RT-PCR products of p53. Asterisks in both panels B and C indicate p53β. (C) HeLa cells were transfected with the empty or FLAG-Y14 expression vector without or with addition of siRNA targeting eIF4A3 or Magoh. RT-PCR of p53 and GAPDH was performed as in panel B. (D) Schematic diagrams for the wild-type and mutant p53 minigenes (p53mini) and the 6 × MS2-containing minigene (p53mini-MS2). Red asterisks indicate 5′ splice sites subjected to mutagenesis. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with control or Y14 siRNA with (lanes 3, 4) or without (lanes 1, 2) the p53 minigene. Primers used for RT-PCR of the p53mini transcripts were CMV and P2. (F) HeLa cells were mock transfected or transfected with a wild-type or mutant p53 minigene as indicated. RT-PCR was as in panel E. Bar graph shows p53β/total p53 ratio; average and standard deviation were obtained from three independent experiments. (G) HeLa or MCF7 cells were transfected with the p53mini-MS2 reporter and the MCP or MCP-Y14-HA expression vector. RT-PCR was as in panel E; MCP-Y14-HA was detected by immunoblotting (IB) with anti-HA.