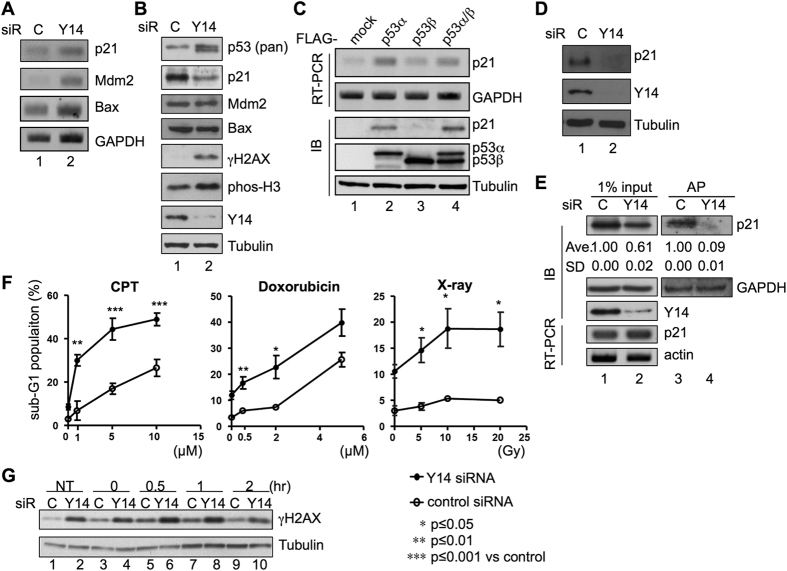
Figure 5. Depletion of Y14 reduces the p21 protein level and increases cell sensitivity to DNA-damaging treatment.
(A) Immunoblotting of p53 and p21, Mdm2, Bax, phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) and H3 (phos-H3), Magoh, Y14, and α-tubulin in control or Y14 siRNA-transfected HeLa cells. (B) RT-PCR analysis of p21, Mdm2, Bax, and GAPDH mRNAs in the samples as in panel A. (C) The p53α and p53β expression vectors were transfected individually (lanes 1 and 2, respectively) or co-transfected (lane 3) in HeLa cells. RT-PCR shows p21 and GAPDH mRNAs. Immunoblotting (IB) shows p21, transiently expressed p53 proteins, and α-tubulin. (D) H1299 cells were transfected with control or Y14 siRNA. Immunoblotting shows p21, Y14 and α-tubulin. (E) HeLa cells were transfected with the control or Y14 siRNA followed by metabolic labeling with L-azidohomoalanine. After biotinylation and affinity purification (AP) using streptavidin Sepharose, bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting using antibody against p21 and GAPDH. Protein and RNA in 1% lysates were also analyzed by RT-PCR and immunoblotting, respectively. The level of p21 protein in Y14-depleted cells relative to that of control cells was indicated; the averages and standard deviations were obtained from three experiments. (F) Line graphs show sensitivity of control (open circle) or Y14-depleted (closed circle) cells to different doses of camptothecin, doxorubicin, or X-rays. The values represent the mean and standard deviation obtained from at least three independent experiments; p-values: * < 0.05, ** < 0.01, *** < 0.001. (G) Control or Y14-depleted cells were not treated (NT, lanes 1, 2) or irradiated with 2 Gy of X-rays, and cells were collected at the indicated time points post-irradiation (lanes 3–10). Immunoblotting was performed to detect phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) and α-tubulin.