Fig. 1.
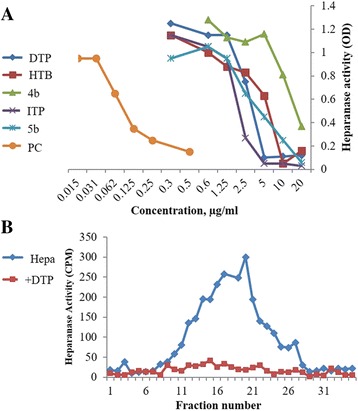
a Screening of compounds for inhibition of heparanase enzymatic activity applying the Fondaparinux heparanase assay. PC, positive control = N-(4-{[4-(1H-Benzoimidazol-2-yl)-arylamino]-methyl}-phenyl)-benzamide [22]. b Lead molecules which exhibited inhibitory activity against human heparanase were validated using a semi-quantitative assay that measures release of radioactive heparan sulfate fragments from an insoluble extracellular matrix as described in ‘Methods’ section. Briefly, sulfate [35S] labeled ECM was incubated (6 h, 37 °C, pH 6.0) with recombinant human heparanase (200 ng/mL) in the absence and presence of 10 μg/mL of the test compounds. Sulfate labeled material released into the incubation medium was subjected to gel filtration on Sepharose 6B. Compound DTP effectively inhibited the cleavage and release of heparan sulfate degradation fragments
