Figure 3.
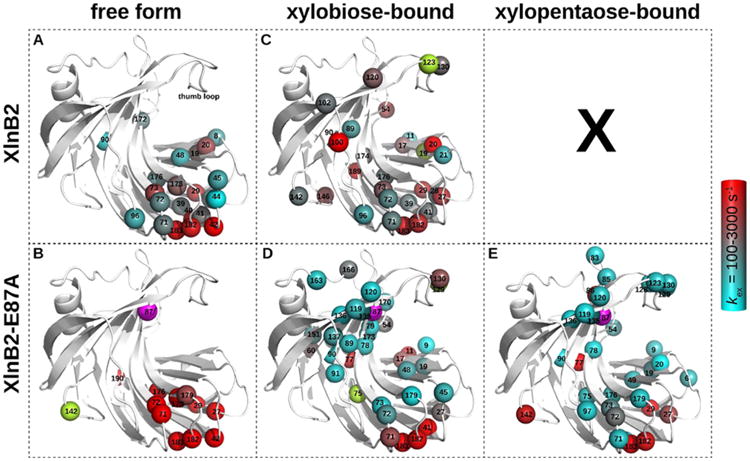
Residues experiencing conformational exchange in the free and ligand-bound forms of XlnB2 and XlnB2-E87A. Conformational exchange was probed using 15N-CPMG NMR relaxation dispersion for XlnB2 and its catalytically impaired variant E87A in the (A and B) free, (C and D) xylobiose-saturated (X2), and (E) xylopentaose-saturated (X5) forms. Residues with a ΔR2(1/τcp) of >1.8 s–1 are reported as spheres on the 3D structure of the enzyme. The color-graded scale represents the rate of conformational exchange (kex) experienced by the backbone 1H–15N vector, calculated on a per residue basis using the single-quantum 15N-CPMG equation.63 Residues with a ΔR2(1/τcp) of >1.8 s–1 for which a kex could not be extracted are colored light green. The mutation site (E87A) is represented as a magenta sphere. All images were prepared with PyMOL. Representative relaxation dispersion curves for each system are shown in Figure S2.
