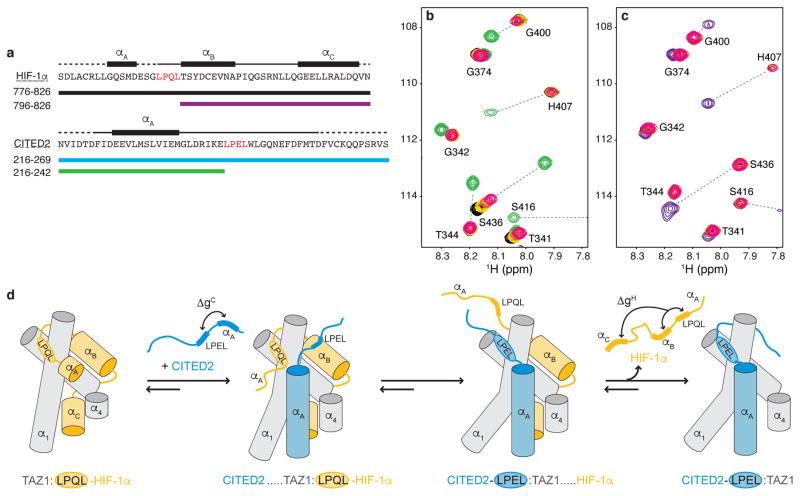
Figure 4. The conserved LP(Q/E)L motif mediates competition between HIF-1α and CITED2.
a, Amino acid sequences of HIF-1α (top) and CITED2 (bottom) transactivation domain peptides and locations of helical motifs. The LP(Q/E)L motif is shown in red. Truncated constructs are indicated by colored bars. b, Superimposed 1H-15N HSQC spectra of 100 μM 15N-TAZ1 in the presence of one molar equivalent of HIF-1α peptide (black), five molar equivalents of CITED2 216-242 (green), and one molar equivalent of HIF-1α peptide plus one (gold), three (orange), or five (magenta) molar equivalents of CITED2 216-242. c, Superimposed 1H-15N HSQC spectra of 100 μM 15N-TAZ1 in the presence of one molar equivalent of CITED2 peptide (cyan), five molar equivalents of HIF-1α 796-826 (purple), and one molar equivalent of CITED2 peptide plus one (gold), three (orange), or five (magenta) molar equivalents of HIF-1α 796-826. The cyan, gold, orange, magenta spectra cross peaks are almost exactly superimposed. d, Schematic mechanism for displacement of HIF-1α from its complex with TAZ1 by CITED2. The α1, α3, and α4 helices of TAZ1 are represented as gray cylinders, HIF-1α is shown in orange, and CITED2 in blue. ΔgC and ΔgH represent thermodynamic coupling23 between the αA and LPEL motifs of CITED2 and between the LPQL-αB and αC motifs of HIF-1α, respectively.