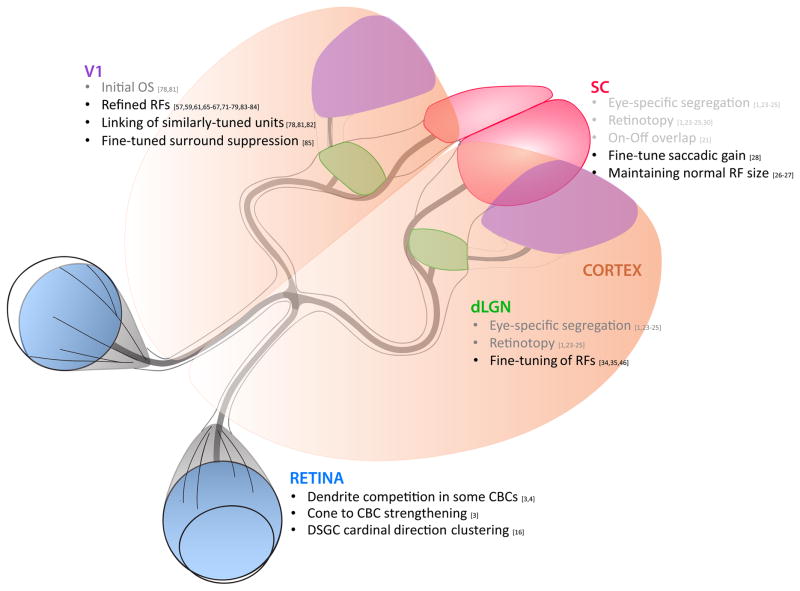
Figure 1.
Summary of major activity-dependent receptive field features at each anatomical station in the mouse visual pathway, from the retina to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (dLGN) and superior colliculus (SC), and dLGN to visual cortex (V1). Items listed in grey appear to be reliant on activity prior to the onset of vision (such as spontaneous retinal waves), whereas items listed in black appear to depend on vision for proper development.