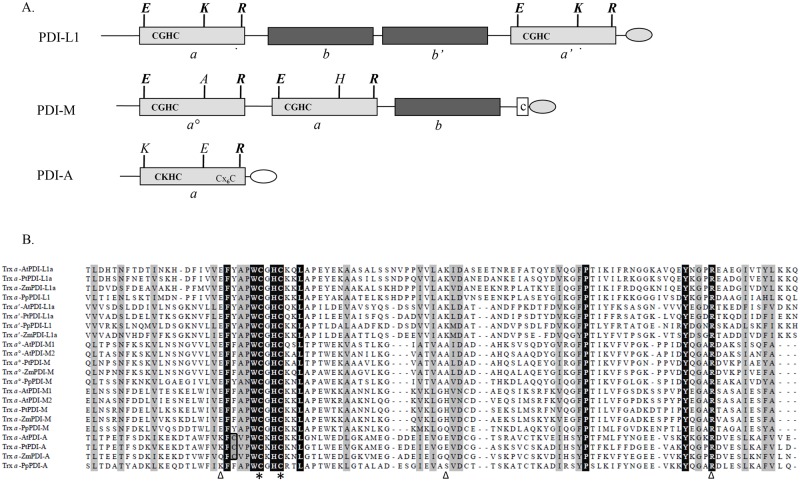
Fig 1. Sequence characteristics and domain organisation of characterized poplar PDI isoforms and their plant orthologs.
A. Modular organisation of poplar PDI-L1a, PDI-M and PDI-A. Boxes in light grey and dark grey indicate redox active (a°, a’ or a) and inactive (b or b’) Trx modules, respectively. Additional letters indicate the amino acids important for the redox properties. The presence of classical (KDEL) ER retention signals are represented in a light grey egg-shaped form. The unusual DK[D/E]L C-terminal sequence found in PDI-A is represented in white. B. Amino acid sequence alignment of the catalytic a modules from PDI-L1a, PDI-M and PDI-A isoforms belonging to At, Arabidopsis thaliana (AtPDI-A, At1g07960; AtPDI-L1a, At1g21750; AtPDI-M1, At1g04980; AtPDI-M2, At2g32920); Pp, Physcomitrella patens (PpPDI-A, Phpat.006G010400; PpPDI-L1, Phpat.015G023600; PpPDI-M, Phpat.004G043700); Pt, Populus trichocarpa (PtPDI-A, Potri.009G004500; PtPDI-L1a, Potri.002G082100; PtPDI-M, Potri.014G160000) and Zm, Zea mays (ZmPDI-A, GRMZM2G073628; ZmPDI-L1a, GRMZM2G091481; ZmPDI-M, GRMZM2G389173). The Trx modules were delimited according to Pfam only database (http://pfam.sanger.ac.uk/) and the alignment was built using ClustalW algorithm at the NPSA web portal (http://npsa-pbil.ibcp.fr). Output of this alignment was made with the ESPript web portal (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/cgi-bin/ESPript.cgi). Amino acids strictly conserved appear in black whereas partially conserved amino acids are indicated in light grey. Cysteines of the active site signature are indicated with stars, The E, K, R residues also represented in the panel A and possibly involved in the modulation of the cysteine pKa are indicated by triangles.