Fig. 2. Parsimony analysis of metazoan steroidogenic pathways.
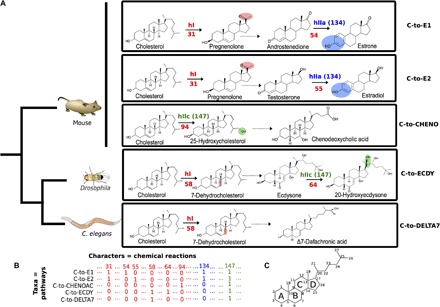
(A) Five examples of metazoan steroidogenic pathways. Some reactions are detailed to explain the character-coding procedure. Some pathways share identical reactions, defined here as type I homologies (hI, in red), such as side-chain cleavage of cholesterol to pregnenolone (reaction 31, in red) in the synthesis of estradiol and estrone (C-to-E1 and C-to-E2 pathways) or dehydrogenation of cholesterol to 7-dehydroxycholesterol (reaction 58, in red) in the C-to-ECDY and C-to-DELTA7 pathways. Some pathways also share similar reactions, defined as type II homologies (hII), with various degrees of similarity. Type IIa homologies (hIIa) describe the same chemical modification at the same place on two different substrates, such as aromatization (character 134, in blue) on androstenedione in the C-to-E1 pathway (reaction 54) or testosterone in the C-to-E2 pathway (reaction 55). Type IIc homologies (hIIc) describe the same chemical modification at different places on two different substrates, such as hydroxylation (character 147, in green) on carbon 25 from cholesterol (reaction 94) in the C-to-CHENO pathway or hydroxylation on carbon 20 from ecdysone in the C-to-ECDY pathway. C. elegans, Caenorhabditis elegans. (B) Extract of the data matrix corresponding to the pathways and steps described above. The presence or absence of characters is coded by 1 and 0, respectively (see complete matrix in fig. S1). (C) Nomenclature of carbon numbers and rings on the sterol skeleton.
