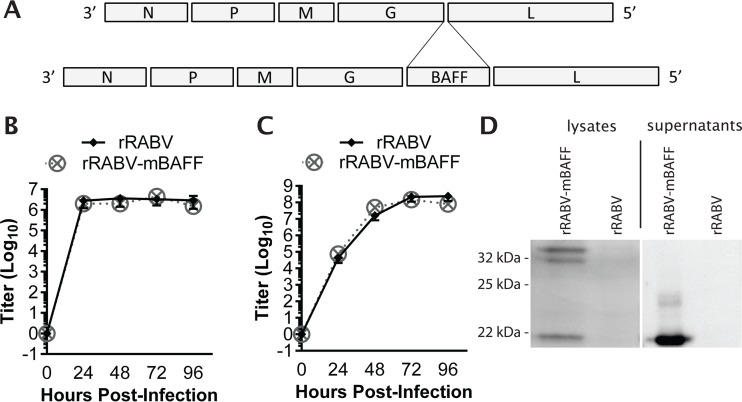
FIG 1.
Construction, recovery, and characterization of a recombinant RABV-based vaccine expressing the murine BAFF gene (rRABV-mBAFF). (A, top) RABV is a molecular clone of the SAD-B19 vaccine strain of rabies. (A, bottom) RABV, which contains two unique restriction sites between the G and the L genes, was spliced with the gene encoding murine BAFF. BSR cells were exposed to rRABV or rRABV-mBAFF at an MOI of 5 for one-step growth kinetics (B) or at an MOI of 0.01 for multicycle growth kinetics (C). Aliquots of cell culture supernatants were collected and viral titers were determined in duplicate for each time point. (D) Expression of BAFF by rRABV-mBAFF was confirmed by Western blotting. BSR cells, which do not endogenously express BAFF, were infected with rRABV or rRABV-mBAFF and lysed 72 h later. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a polyvinylidene membrane, and immunodetection with antibodies specific for BAFF was performed. A protein of the expected size for full-length and cleaved soluble BAFF was detected in lysates of rRABV-mBAFF-exposed but not from rRABV-exposed BSR cells. In parallel, purified and concentrated BSR cell supernatants were analyzed by Western blotting. A protein of the expected size of soluble BAFF was detected in rRABV-mBAFF-exposed but not in rRABV-exposed BSR cell supernatant.