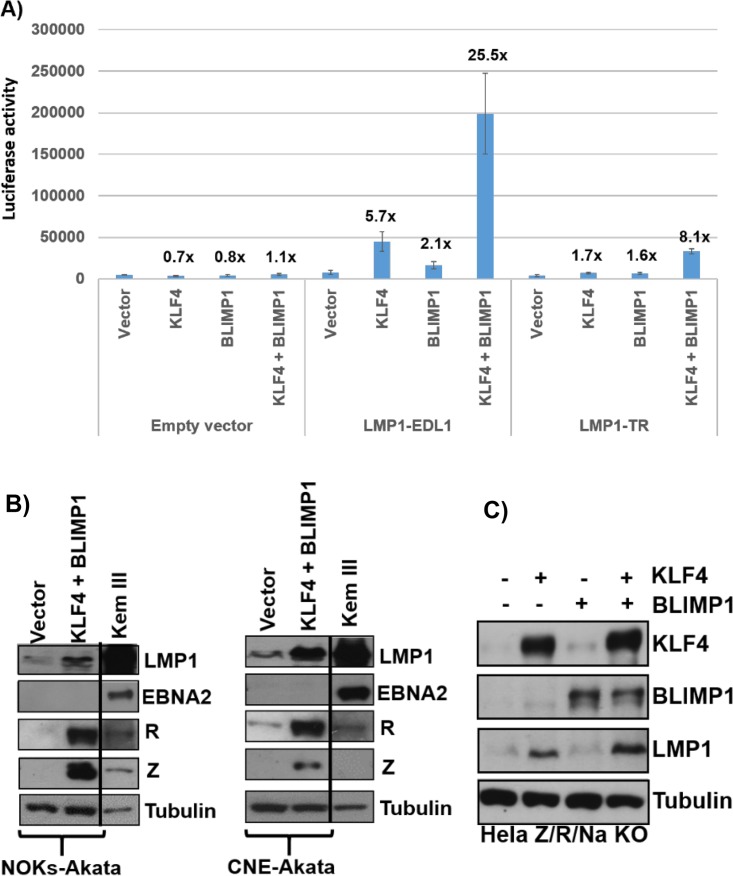
FIG 8.
KLF4 and BLIMP1 synergistically activate the LMP1 promoters. (A) Reporter gene constructs containing either the proximal LMP1 promoter (LMP1-EDL1), the distal LMP1 promoter (LMP1-TR), or no promoter sequences upstream of the luciferase gene were cotransfected into EBV-negative NOKs cells with either the control vector, the KLF4 vector alone, the BLIMP1 vector alone, or the combination of the KLF4 and BLIMP1 vectors. Luciferase assays were performed 2 days after transfection. Total luciferase activity for each of the conditions from a representative experiment is shown (data are averages ± standard deviations of results from three replicates), as well as the fold increase in activity induced by KLF4 or BLIMP1. Similar results were obtained in three separate experiments. (B) NOKs-Akata cells (left) or CNE-Akata cells (right) were transfected with either the control vector or the KLF4 and BLIMP1 expression vectors, and immunoblotting was performed to detect LMP1, EBNA2, Z, R, and tubulin. Kem III cells served as the positive control for EBNA2 and LMP1. (C) HeLa cells infected with a mutant EBV strain with deletions of the Z/R/BRRF1 genes were transfected with either the control vector or the KLF4 and BLIMP1 expression vectors (either alone or in combination). Immunoblot analysis was performed to compare the levels of transfected KLF4 and BLIMP1 and the induction of EBV LMP1 from the EBV genome. The cellular protein tubulin was used as a loading control.