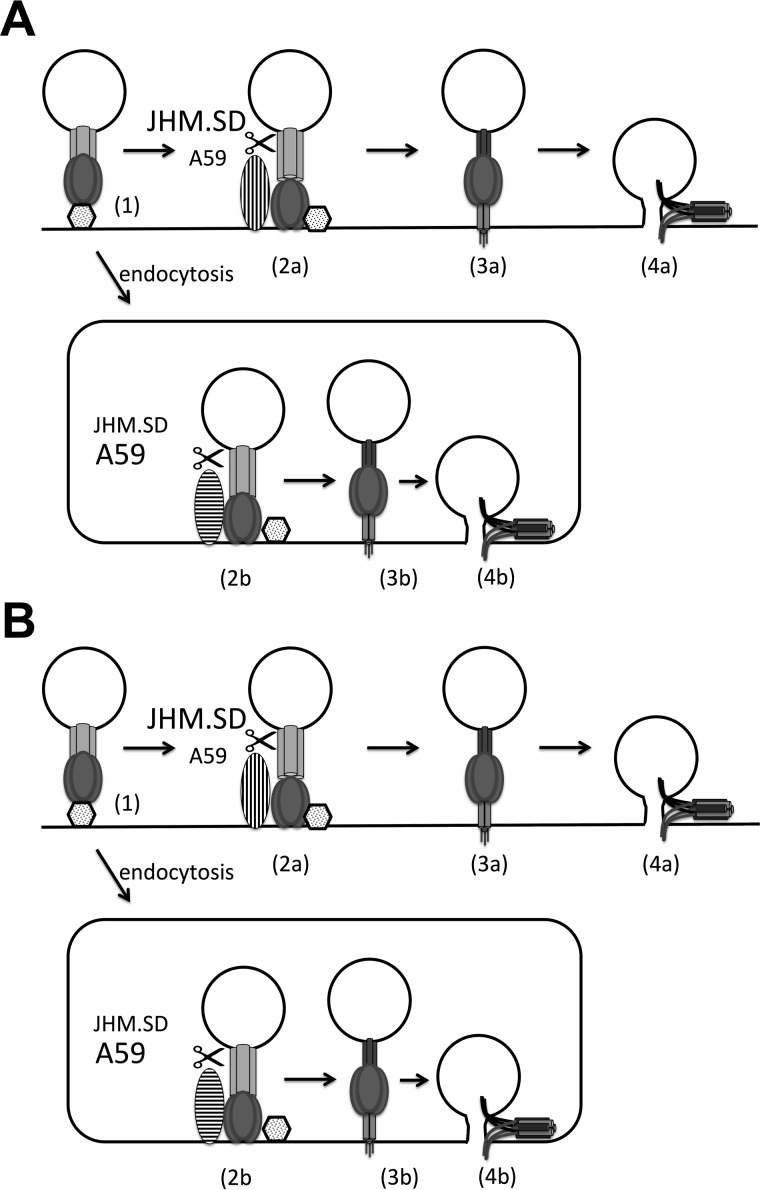
FIG 9.
Independent and sequential cleavage models of MHV entry. (A) In the independent pathway model, JHM.SD is more efficiently cleaved by cell surface acid-independent proteases (vertical stripes) such as metalloprotease or TMPRSS2 and fuses at the plasma membrane, whereas A59 better survives endocytosis and/or is more efficiently cleaved by acid-dependent endosomal proteases (horizontal stripes). In the sequential cleavage model (B), cleavage by acid-independent proteases produces a metastable intermediate that is more readily cleaved by endosomal proteases, and JHM.SD S is more efficiently cleaved by acid-independent proteases but less efficiently cleaved by endosomal proteases.