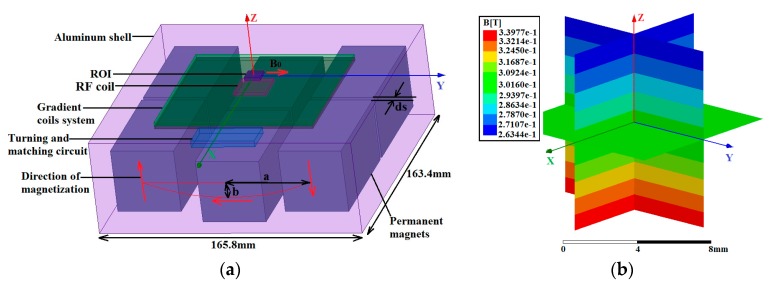
Figure 1.
(a) Newly reduced Halbach magnet equipped with a 2D gradient coil system. This magnet was created by utilizing six NdFeB magnet blocks. The polarization directions of the magnets and main field are indicated by red arrows. The six magnets are polarized along the −z-, −y-, and +z-directions. The magnets pointing in the same polarization direction were separated by a small gap ds, whereas the magnets pointing to different polarization directions formed a reduced Halbach structure and were positioned in an elliptical arc. The ratio of the semimajor axis a to the semiminor axis b was 2.3. (b) Simulation results of the optimized reduced Halbach magnet structure. The magnetic field was computed using the Ansoft finite element method (FEM) software. The calculated magnetic field is shown for distances to the center of the six-magnet array lower than 5 mm and above the magnet array surface at 10–20 mm. At the target plane, the simulated magnetic magnitude was about 0.299 T points along y, and the constant gradient was approximately 7.6 T/m points along z. A homogeneous magnetic field was produced on the horizontal target plane.