Figure 1.
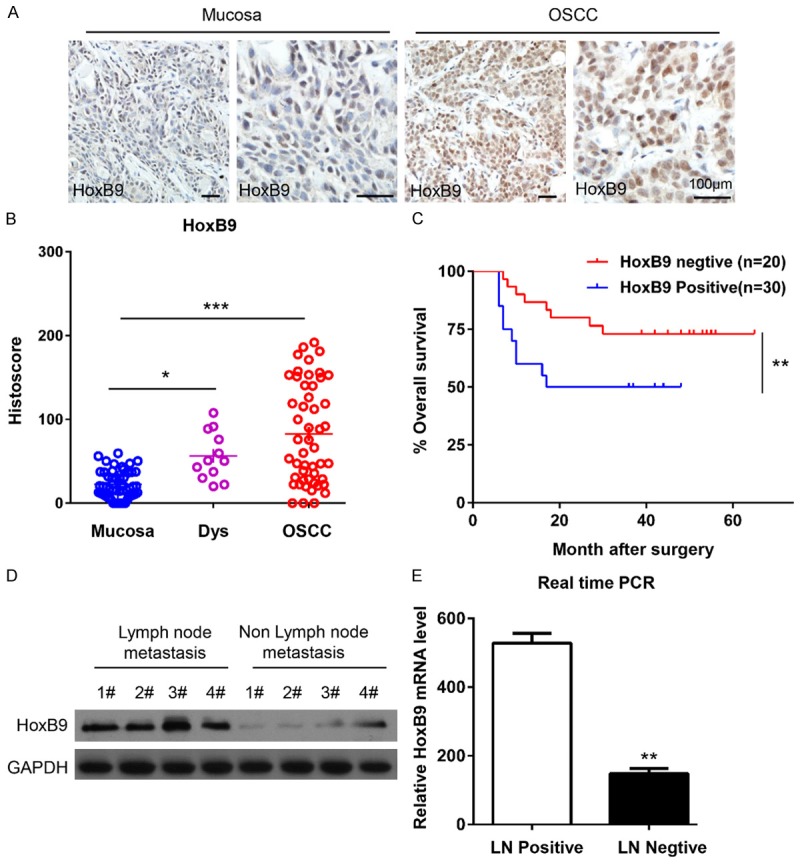
HoxB9 expression was up-regulated in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). A. Representative immunohistochemical staining of HoxB9 in human OSCC tissue (right panel) compared with normal mucosa (left panel; scale bars = 100 μm). B. Quantification of HoxB9 expression levels in human mucosa, dysplastic tissue and OSCC tissue (*P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001; one-way ANOVA with GraphPad Prism 5.0). C. Kaplan-Meier curve of overall survival of 50 patients with OSCC stratified by the expression level of HoxB9. The duration of survival was measured from the beginning of the treatment to the time of death or at the final follow-up (60 months). The cumulative survival for patients with HoxB9-positive OSCC was significantly lower than that for patients with HoxB9-negative OSCC (**P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA with GraphPad Prism 5.0). D. Western blot analysis of the protein expression of HoxB9 in patients with or without lymph node metastasis, GAPDH was used as a loading control. E. The relative mRNA levels of HoxB9 were detected by RT-PCR in patients with or without lymph node metastasis. The data are presented as the means ± SEM. One-way ANOVA with post-Dunnett analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 5.0. **P < 0.01 versus the control group (n = 3).
