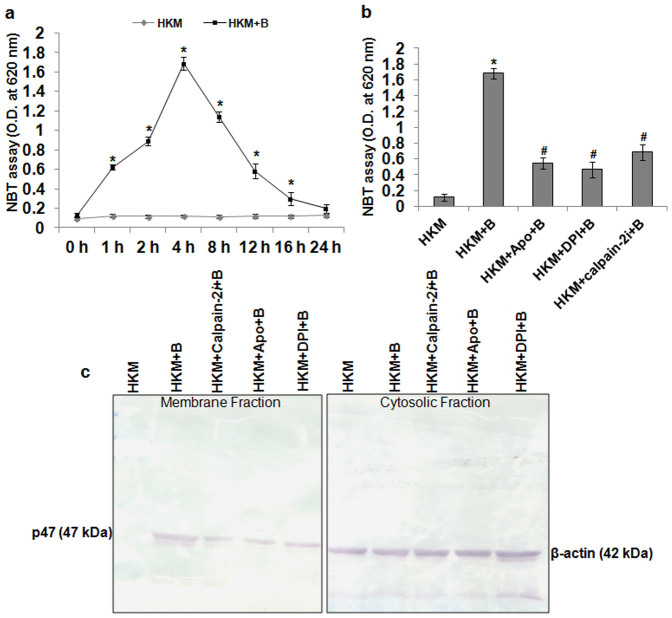
Figure 2. Calpain-2 induces NADPH Oxidase mediated superoxide ion production in A. hydrophila-infected HKM.
(a) HKM were infected with A. hydrophila and at indicated time p.i. superoxide ion production measured by NBT assay. Statistically significant amount of superoxide ion was detected at 1 h p.i. and it continued till 16 h p.i. (*P < 0.001/F = 341.6). (b) HKM were pre-treated separately with Apo, DPI and calpain-2i and superoxide ion production measured at 4 h p.i. Pre-treatment with the inhibitors significantly lowered superoxide ion production in the infected-HKM (*, #P < 0.001/F = 125.4). (c) HKM were pre-treated separately with Apo, DPI and calpain-2i and at 4 h p.i. p47phox membrane translocation studied by immunoblotting. The cytosolic fraction was probed with β-actin to confirm for equal loading. *P vs HKM; #P vs HKM + B. Vertical bars represent mean ± SE (n = 6). HKM, uninfected control; HKM + B, HKM infected with A. hydrophila; HKM + Apo + B, HKM pre-treated with Apo for 1 h before A. hydrophila-infection; HKM + DPI + B, HKM pre-treated with DPI for 2 h before A. hydrophila-infection; HKM + calpain-2i + B, HKM pre-treated with calpain-2i for 1 h before A. hydrophila-infection. Apo and DPI, NADPH Oxidase inhibitor; calpain-2i, calpain-2 inhibitor.