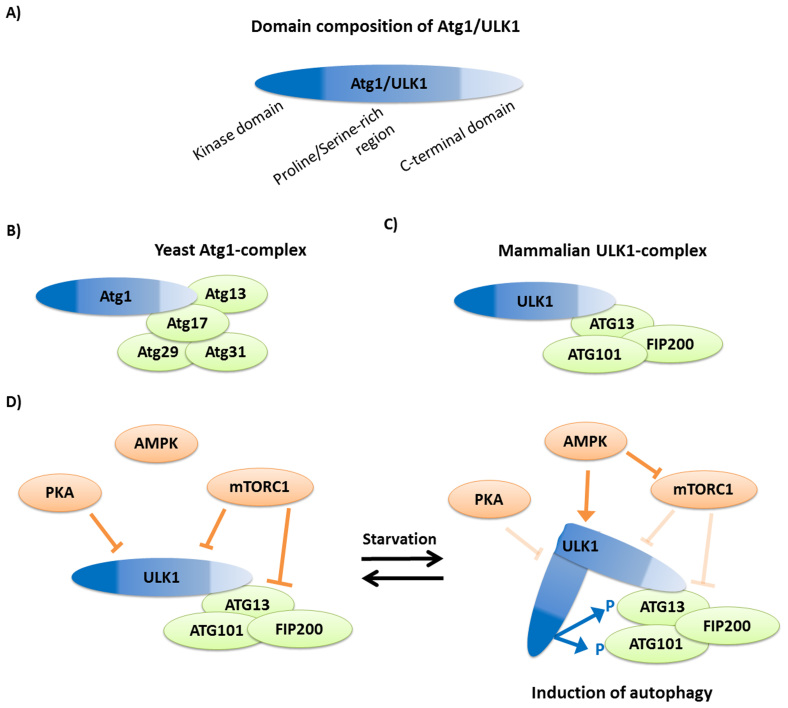
Figure 1. The autophagy induction Atg1 complex in yeast and mammals.
(a) The protein domain composition of Atg1/ULK1. (b) In yeast, the complex contains Atg1, which directly binds to Atg13 and Atg17, while Atg29 and Atg31 are linked to the complex through Atg17. (c) The mammalian complex is formed by ULK1, the ortholog of Atg1, which interacts with ATG13. The two other members of the complex are ATG101 and FIP200. (d) In normal, nutrient rich conditions the mammalian TOR complex 1 (mTORC1) inhibits ULK1 and ATG13 by phosphorylation. This inhibition is enhanced by phosphorylation on ULK1 by another cellular nutrient sensor, the cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA)51. We note that in yeast Tpk1, ortholog of the mammalian PKA, can also phosphorylate Atg1 but this reaction regulates only further steps of the autophagic process and not the induction52. Upon starvation nutrient limitation inhibits PKA and activates AMPK. Activated AMPK inhibits mTORC1 and activates ULK1 by direct phosphorylation53,54. Both reactions enable ULK1 to become active. ULK1 conformation is hypothesized to have an “open” and a “close” conformation19. Active ULK1 may take a close conformation, in which the middle proline/serine-rich regions move the kinase domain to the proximity of its possible targets, ATG13 and FIP200. Their phosphorylation triggers downstream events for autophagosome formation. Figures were made based on Ref. 12.