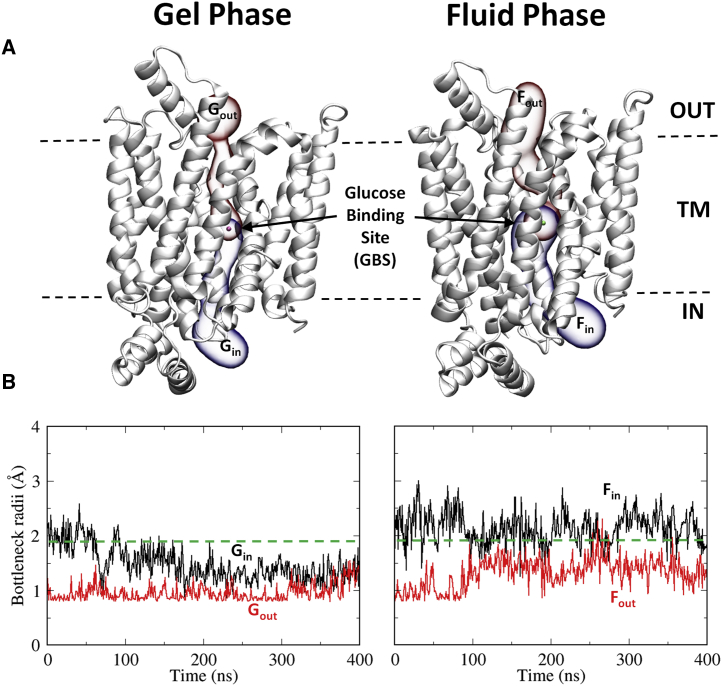
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic representation of the glucose pathway in the protein that extends from the intracellular (IN) to the extracellular (OUT) sides of the membrane through the main glucose-binding site (GBS) at the center of the transporter. The permeation pathway connecting the intracellular part up to the main GBS is shown in blue and labeled with the subscript “in.” The pathway connecting the extracellular side with the main GBS is shown in red and labeled with the subscript “out.” G and F refer to the gel and fluid phases of the membrane, respectively. (B) Evolution of the bottleneck radius of the main cavity running along the transporter with time in each membrane phase. The green discontinuous line indicates the minimal radius of a glucose molecule. To see this figure in color, go online.