Figure 3.
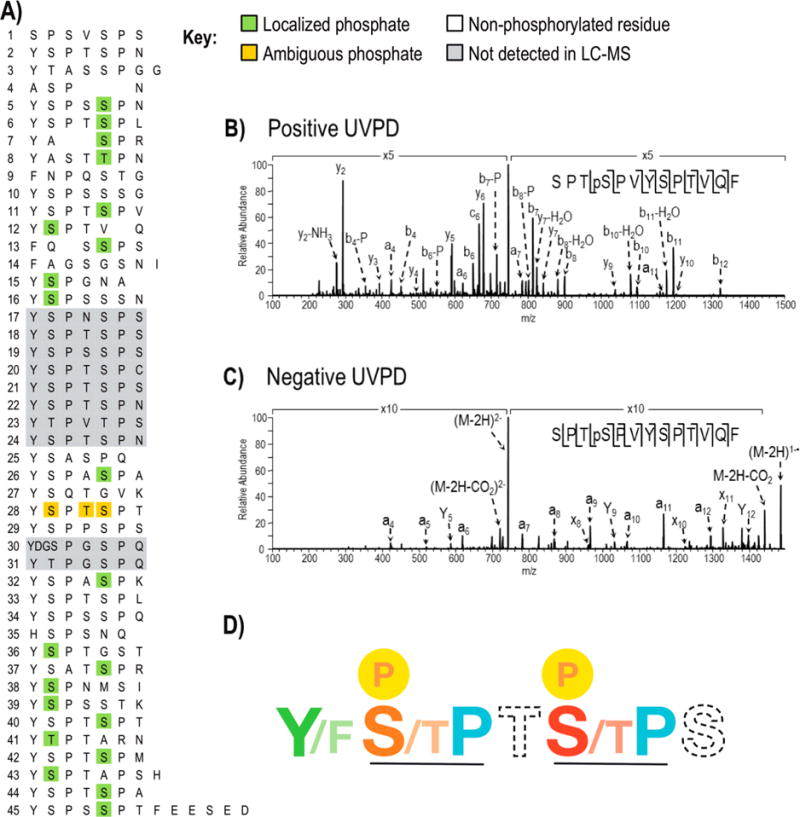
Phosphorylations identified in Drosophila melanogaster CTD following treatment with Erk2 using LC-UVPD-MS. A) The site of phosphorylation in Drosophila melanogaster CTD where confirmed sites are highlighted in green. One peptide (repeat 28) shows a single phosphorylation but the position of the phosphate could not be distinguished among three sites (shown in gold). Regions of the protein in gray were not detected in the Erk2 treated or control CTD samples. The phosphorylation map is the composite of sites identified using positive mode and negative mode LC-UVPD-MS. Representative UVPD mass spectra from positive mode (B) and negative mode (C) analysis are shown for the chymotryptic peptide SPTpSPVYSPTVQF which covers heptads 11 and 12. In both polarities, the doubly charged ions of m/z 745.3 (for positive mode) and m/z 743.3 (for negative mode) were activated using 2 pulses at 2 mJ. Ions that are detected following phosphate neutral loss are denoted by “-P”. D) The “rule book” for CTD phosphorylation by Erk2. SP motifs are recognized with the strict requirement for proline (blue) following serine/threonine (orange and red). Ser5 (S, red) is favored over Ser2 (S, orange) during phosphorylation by Erk2. Thr4 (T) and Ser7 (S) shown in dashed font had little impact on the phosphorylation outcome. An aromatic residue such as tyrosine (Y) or phenylalanine (F) is required (colored green) for phosphorylation.
