Figure 5. Evolutionary relationships of Zfs1 targets within members of the CTG clade.
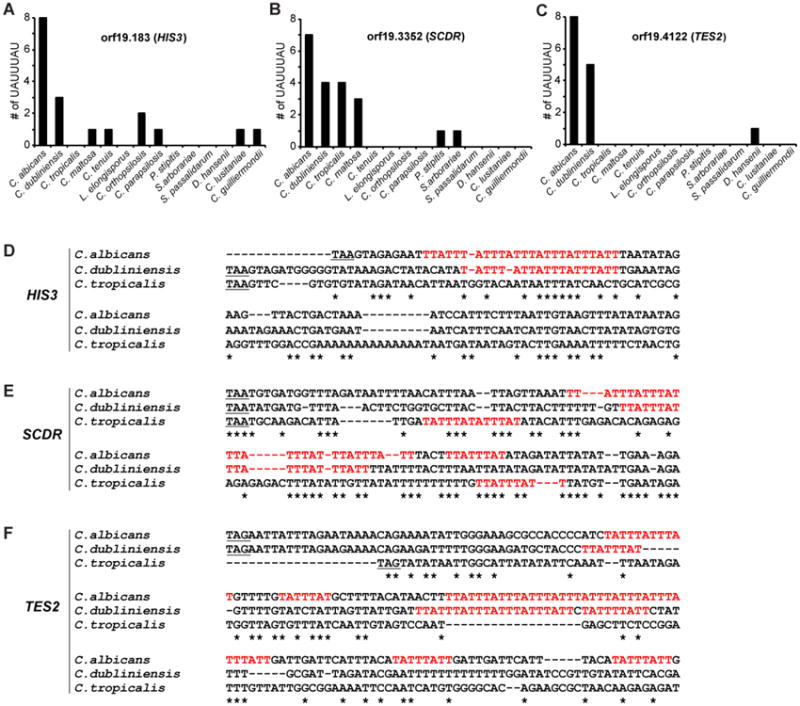
Shown are the numbers of potential 7-mer binding sites within 500 base pairs of the stop codons in transcripts from the orthologues of C. albicans HIS3 (A; orf19.183), SCDR (B; orf19.3352), and TES2 (C; orf19.4122). The order of species along the X-axis roughly reflects increasing evolutionary distance of the species from C. albicans, based on previous phylogenetic comparisons. (D-F) Alignments performed with Clustal Omega of the sequences of the 3′UTRs of (D) HIS3, (E) SCDR, and (F) TES2 from the indicated CTG clade species are shown, including the potential binding 7-mers in red. The alignment begins at the stop codon (underlined) and continues at least 60 bases after the 3′-most 7-mer identified in any of the species. Asterisks (*) indicate sequence identity. Reproduced from [35], with permission.
