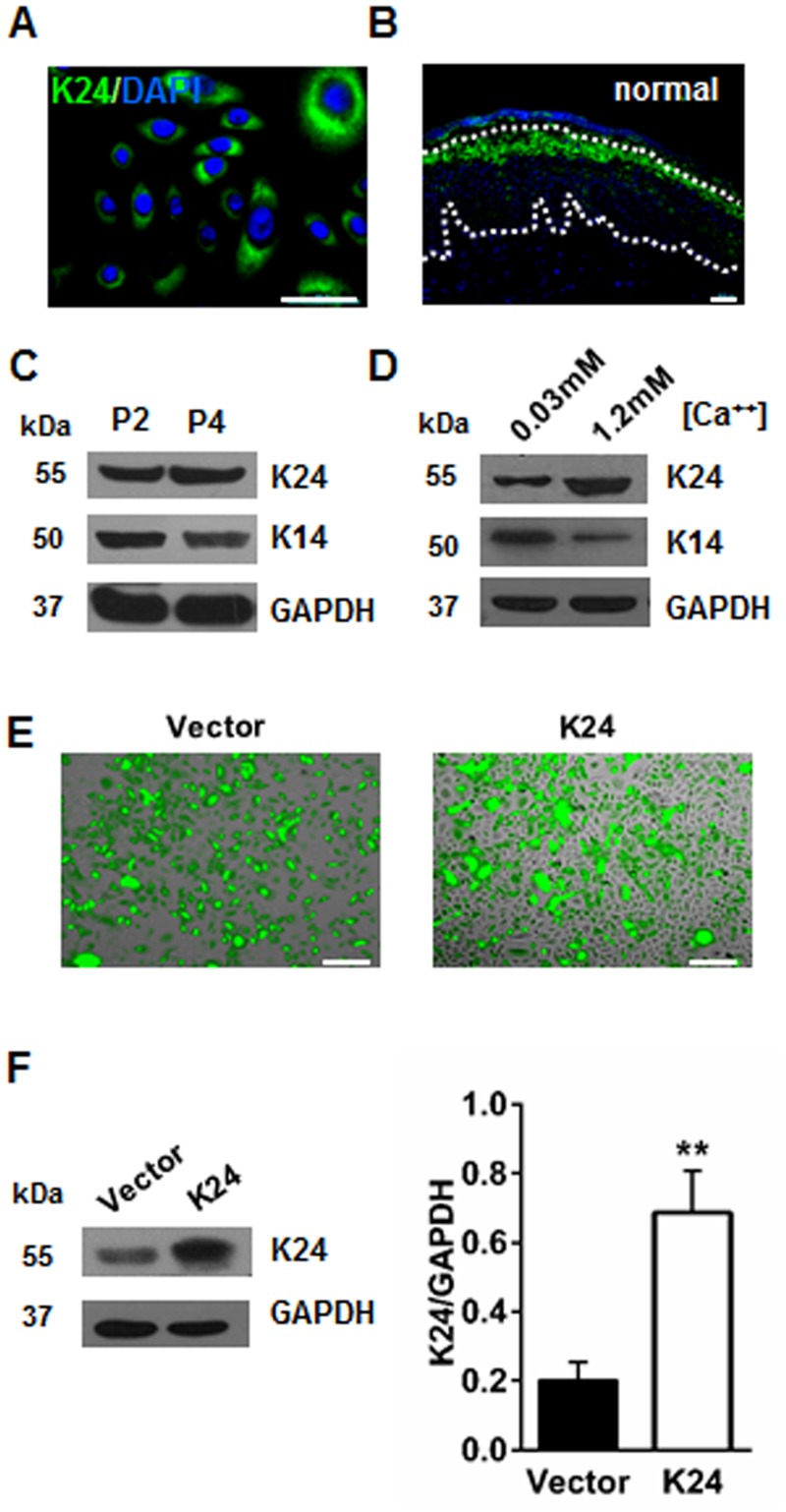
Fig 1. K24 plays an important role in the differentiation of NHEK.
(A) Immunofluorescent staining of NHEK by K24 antibody. Green: K24; Blue: DAPI; Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of normal epidermis by K24 antibody. Scale bar = 50 μm. Negative control images in which the primary antibody for rabbit IgG was used only are shown in S1 Fig. Enlarged immunofluorescent image of normal epidermis stained by K24 antibody is shown in S2 Fig. (C) Western blot analysis of K24 and K14 protein levels in subcultured 2nd passage(P2) and 4th passage(P4) primary keratinocytes. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (D) Western blot analysis of K24 and K14 protein levels in NHEK following differentiation in 1.2 mM (high Ca+) and 0.03mM CaCl2(low Ca+) for 4 days. Similar results were observed in three independent experiments. (E)Pictures taken at 24h after K24 lentivirus transfection in NHEK cells. The transfection rate was over 80% in all experiments as demonstrated by GFP production. Scale bar = 50μm. (F)K24 protein levels in NHEK transfected with control vector and K24 overexpression vector were measured by western blot analysis. Quantification of K24 protein level in two groups are shown in the histogram. Vector: vector control group, K24: K24 overexpression group. GAPDH was used as the internal control. Data were expressed as mean ± s.e.m. Student t-test was used, **p<0.01vs vector control. The experiment was repeated with primary keratinocytes derived from five different donors.