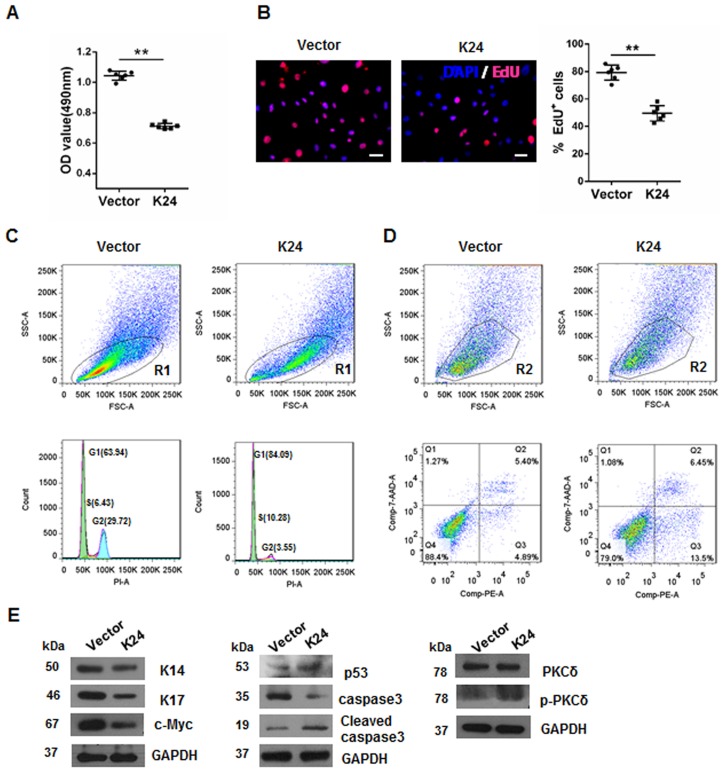
Fig 2. Overexpression of K24 in NHEK reduces cell growth, blocks cell cycle progression, and induces apoptosis.
(A)Effect of K24 overexpression at 24h after transfection on cell proliferation measured by MTS assay (n = 6). Similar results were observed in three independent experiments. (B)Representative pictures of EdU incorporation in NHEK transfected with either vector or K24 lentivirus are shown. The values of EdU+% cells were determined in histogram. EdU is in red and Hoechst is in blue. Scale Bar = 100 μm. n = 6. The experiments were repeated three times with similar results. In (A) and (B), the Student t-test was used, **p<0.01 vs the vector control. (C)Representative pictures shows effect of K24 overexpression on cell cycle measured by cytometry analysis. Cells that fall into the R1 gate were selected for cell cycle analysis of total cells. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (D)Representative pictures shows effect of K24 overexpression on the cell apoptosis rate determined by flow cytometry. Cell populations were gated (R2) as shown, the annexin V-positive cells are the cells undergoing apoptosis and are represented in the lower right quadrant. Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments. (E)Effect of K24 overexpression on the levels of K14, K17, c-Myc, p53, caspase3, PKCδ and p-PKCδ were measured by Western blot analysis with GAPDH protein as the internal control. The experiment was repeated with primary keratinocytes derived from three different donors.