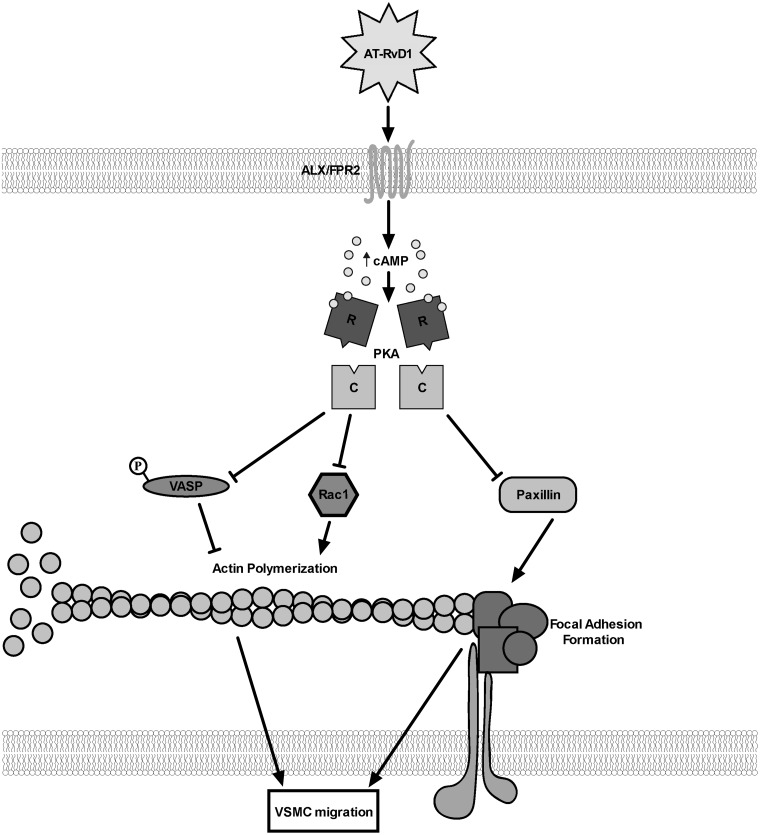
Fig 9. Schematic of proposed pathway by which RvD1 modulates VSMC migration.
The schematic shows a summary of our findings in a proposed simplified mechanism for the effects of AT-RvD1 on VSMC migration. AT-RvD1 increases cAMP levels at least by activating ALX/FPR2; the subsequent activation of PKA interferes with actin polymerization by inhibiting VASP (by phosphorylation) and Rac1, and with focal adhesion formation by decreasing paxillin localization to the cell leading edge. “R” and “C” represent the regulatory and the catalytic subunits of PKA, respectively.