-
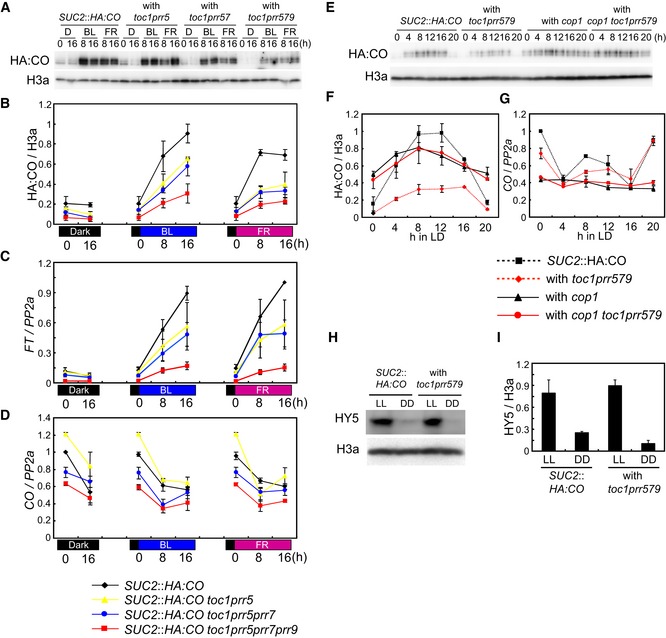
A, B
Effect of double, triple, and quadruple prr mutations on HA:CO protein accumulation in blue light (BL) and far‐red light (FR). Plants were grown under LDs and then transferred to darkness for 24 h. The plants were then transferred to continuous BL or FR at ZT 0. A population of plants was kept in darkness (D) as control. HA:CO protein was analyzed in each genotype at the illustrated times under BL, FR, or control D treatment.
-
C
FT mRNA accumulation under the same conditions as in (A, B).
-
D
CO mRNA accumulation under the same conditions as in (A, B).
-
E–G
PRRs suppress ability of COP1 to degrade CO. (E, F) Effect of quadruple prr, cop1, and quintuple prr/cop1 mutations on CO protein abundance in SUC2::HA:CO background through a time course under LDs. (G) CO mRNA levels in genotypes used in (F).
-
H, I
Abundance of HY5 protein in prr quadruple mutant in continuous light (LL) and continuous dark (DD). Plants were grown under LDs for 7 days, transferred to LL or DD at ZT 0 and kept for 40 h before harvesting.
Data information: The values of HA:CO and HY5 levels were normalized to those of histone 3a. Student's
t‐test revealed no significant difference between genotypes. The values of
CO and
FT mRNA levels were normalized by those of
PP2a. For all data except for (B), error bars indicate standard error within two biological replicates. For (B), error bars indicate standard error within three biological replicates. For the RNA analyses, two technical replicates were performed in each biological replicate.