Figure 3. EDD‐DYRK2‐DDB1Vpr BP is present at the centrosome and mapping functional domains of Cep78 and VprBP .
-
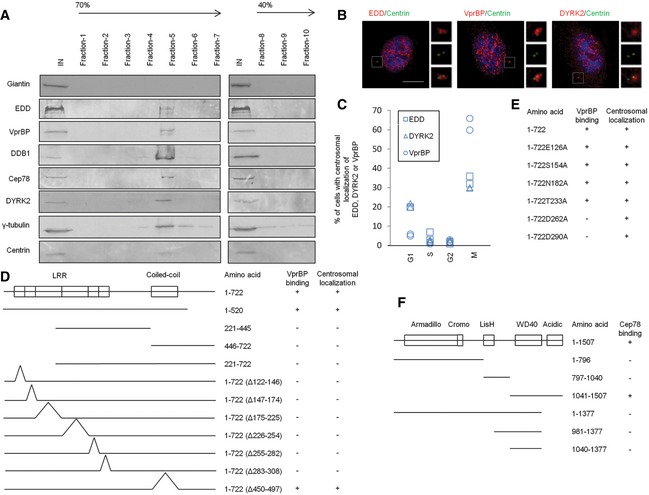
ACentrosomes from Jurkat cells were purified through a 40–70% sucrose gradient, and the resulting fractions were Western blotted with the indicated antibodies. IN, input. γ‐tubulin and centrin, positive control; giantin, negative control.
-
BRPE‐1 cells were stained with DAPI (blue) and antibodies against centrin (green) and EDD, DYRK2 or VprBP (red). Scale bar, 1 μm.
-
CThe percentage of cells with centrosomal EDD, DYRK2, or VprBP staining across the cell cycle. At least 100 cells were scored in each cell cycle phase and two independent experiments were performed.
-
D, EThe ability of various Cep78 truncated, deletion, and point mutants to interact with VprBP and localize to centrosomes. 1–722, full‐length; Δ122–146, deletion of the first LRR repeat; Δ147–174, deletion of the second LRR repeat; Δ175–225, deletion of the third LRR repeat; Δ226–254, deletion of the fourth LRR repeat; Δ255–282, deletion of the fifth LRR repeat; Δ283–308, deletion of the sixth LRR repeat; Δ450–497, deletion of the coiled‐coil domain. E126A, S154A, N182A, T233A, D262A, and D290A, point mutations of the first, second, third, fourth, fifth, and sixth LRR repeats, respectively.
-
FThe ability of various VprBP truncates to interact with Cep78. 1–1,507, full‐length.
Source data are available online for this figure.
