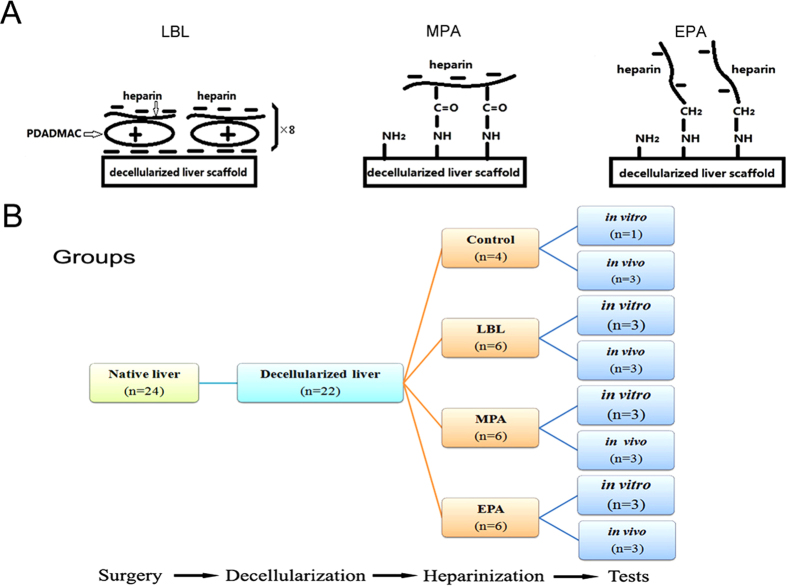
Figure 1. Experiment design.
(A)Schematic of the structures of heparin immobilized on decellularized liver scaffolds (DLSs). (left) the DLS immobilized with heparin using the layer-by-layer (LBL) technique; (middle) the DLS covalently immobilized with heparin using the multi-point attachment (MPA) technique; (right) the DLS covalently immobilized with heparin using the end-point attachment (EPA) technique. (B) Flow chart of the anticoagulation of DLSs through heparin immobilization experiment. The 22 whole livers were perfusion decellularized successfully out of 24 isolated livers from mini-pigs (weight 10–15 kg). The 18 DLSs were divided into 3 groups for LBL, MPA or EPA heparin immobilization, respectively. In each group, half of heparinized DLSs (n = 3) were transplanted into recipient mini-pigs (weight 23–25 kg), and the other half (n = 3) was used for examination in vitro. Non-heparin treated DLSs were used as control.