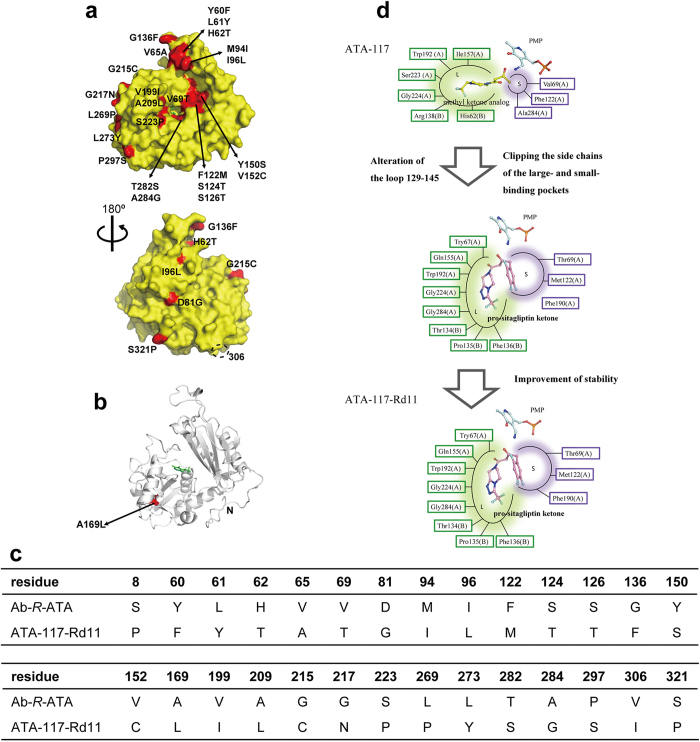
Figure 3. Analysis of the previous molecular engineering of ATA-117.
(a-c) Amino acid sequence comparison among Ab-R-ATA, ATA-117, and ATA-117-Rd11. The 27 mutations introduced in the previous successful engineering of ATA-117 on the molecular surface (a) or inside the molecule (b) are highlighted in red and labeled. Residue 306 is indicated by the dashed circle in (a) .The “N” in (b) represents the Val11 at the N-terminus. The unobserved Phe8 in ATA-117-Rd11 is probably away from the active site. The cofactor PLP in the active site is shown as green sticks. The table in (c) shows the differences of the amino acid residues among three R-ATAs. (d) A schematic diagram of the strategies in the engineering. The amino acid residues consisting of the L pocket and S pocket are represented in green and purple text boxes, respectively. Cofactor PMP and docked ligands are shown as sticks.