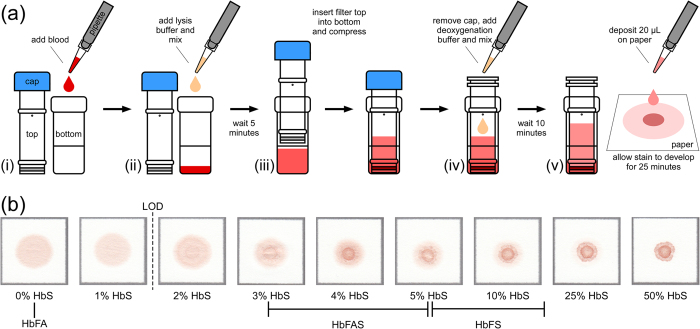
Figure 2. Paper-based newborn SCD screening test.
(a) Schematic illustration of the steps required to perform the newborn paper-based test: (i) 20 μL of whole blood collected via heel-stick is added to the bottom chamber of the syringeless filter; (ii) the blood is mixed with lysis buffer (phosphate buffer and saponin); (iii) after 5 min the top of the syringeless filter is inserted into the bottom and compressed to filter out cellular debris; (iv) deoxygenation buffer (phosphate buffer and sodium hydrosulfite) is added to the filtered solution; (v) after 10 min a 20 μL drop of the mixture is deposited on chromatography paper and allowed to dry for 25 minutes. All steps required to perform the test can be completed within 40 min. Test results can also be read out visually, immediately after the formation of the blood stain. (b) Representative bloodstains produced on paper by the paper-based newborn SCD screening test for blood samples with various sickle hemoglobin (HbS) levels. The limit of detection (LOD; dashed line) for detecting the presence of any HbS in a blood sample visually was 2%. Typical newborn HbS ranges for different genotypes are marked below the stains.