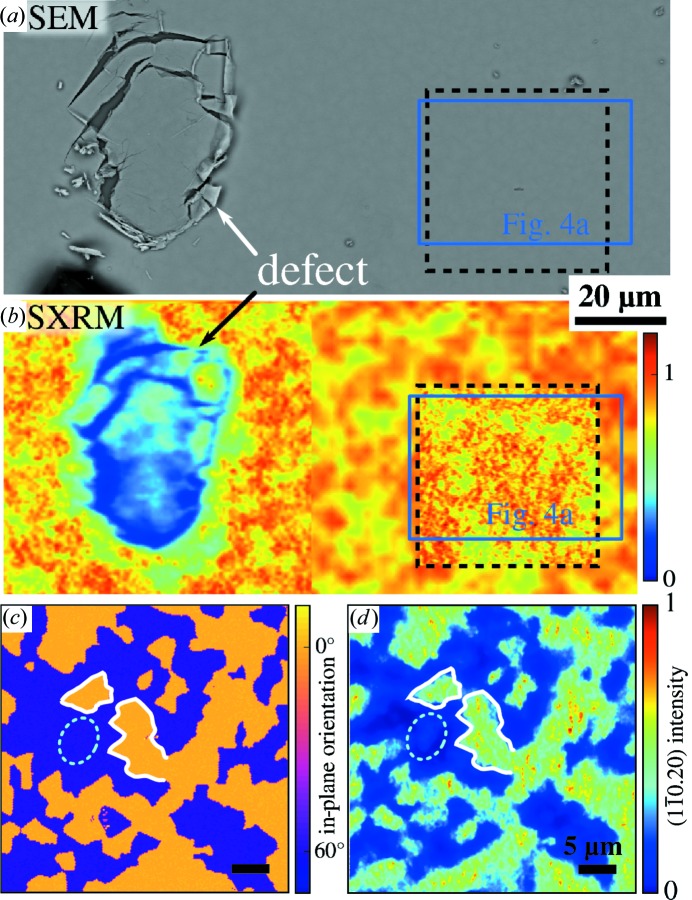
Figure 5.
Comparison of SXRM and EBSD twin maps of the same position on Bi2Te3 sample BT-B. SEM (a) and SXRM (b) using a symmetric Bragg peak are used to localize the same area on the sample surface for both methods. The position of the EBSD map shown in Fig. 4 ▸(a) is marked by a blue rectangle, while a dashed rectangle indicates the location of the EBSD/SXRM measurements shown in (c) and (d), respectively. For the SXRM image in (b) the symmetric (000.15) Bragg peak was used to be insensitive to the twin domain pattern. (c) and (d) show the in-plane crystal orientation determined by EBSD, i.e. the direction of the a axis/[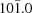 ], and an SXRM image of the same area produced by the asymmetric (
], and an SXRM image of the same area produced by the asymmetric (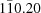 ) Bragg peak. The white lines in (c) and (d) mark the same features while the dashed ellipse highlights some distinctions.
) Bragg peak. The white lines in (c) and (d) mark the same features while the dashed ellipse highlights some distinctions.