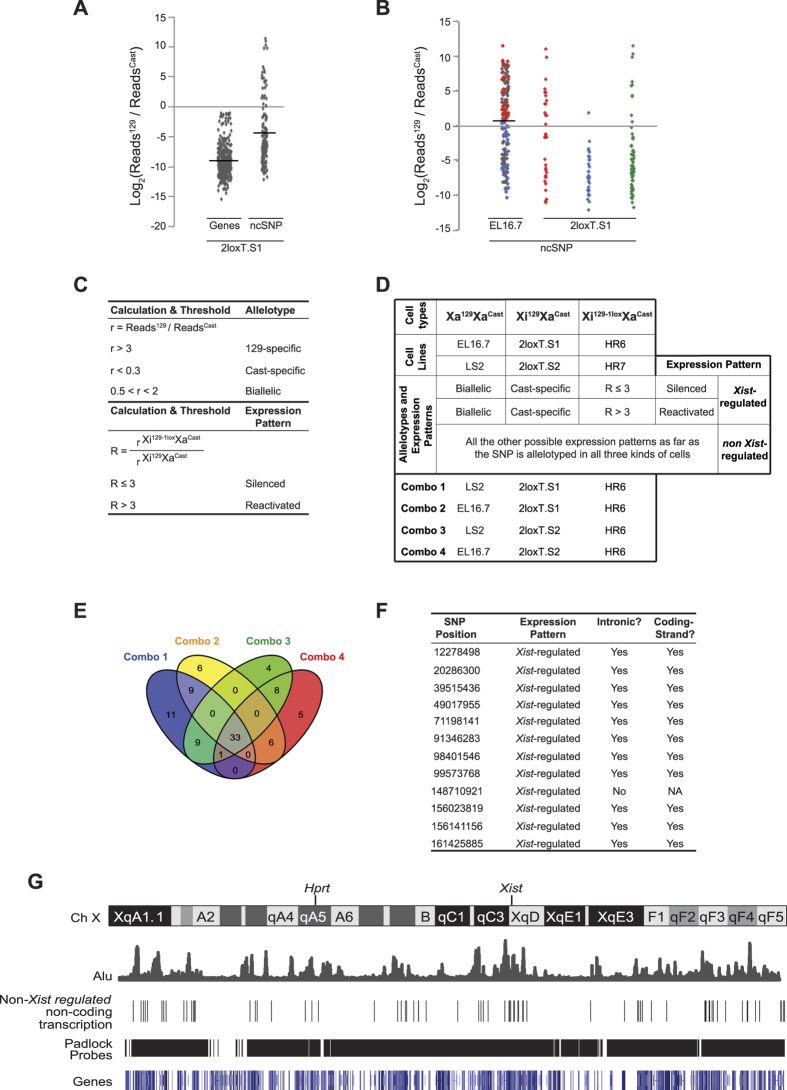
Figure 3. Non-coding transcription along the Xi is largely independent from Xist-mediated gene silencing.
(A) The allelotype of X-linked ncSNPs and X-linked genes in 2loxT.S1 cells. (B) The allelotype of X-linked ncSNPs in EL16.7 and 2loxT.S1 cells. The SNPs only allelotyped in one cell type are labeled in gray (EL16.7) and green (2loxT.S1). The SNPs allelotyped in both cell types are labeled in red or blue. The red dots represent the SNPs with an above-average allelotype score in EL16.7. The blue dots represent the SNPs with a below-average allelotype score in EL16.7. The data from 2loxT.S1 cells is grouped into three columns for visualizing the allelotype changes of the ncSNPs before and after XCI. (C) Calculations and thresholds used in analyzing the data of padlock capture of X-linked non-coding transcriptions. (D) The definitions of “expression pattern”, which are used to describe the allele-specific expression profile of an X-linked non-coding SNP. Cell lines of three different genotypes were used in the study. Two cell lines were selected for each genotype. The data from different cell lines were combined in four different ways to test the consistency of the experiments. (E) A Venn diagram showing the non-coding SNPs with “non-Xist regulated” expression pattern from the data analysis of four different combinations of data sets. (F) Non-coding SNPs with “Xist-regulated” expression pattern from the data analysis of four different combinations of data sets. (G) The distributions of genes, Alu elements, padlock probes targeting non-coding regions and the “non-Xist regulated” non-coding transcription activities detected along the mouse X chromosome.