Figure 4.
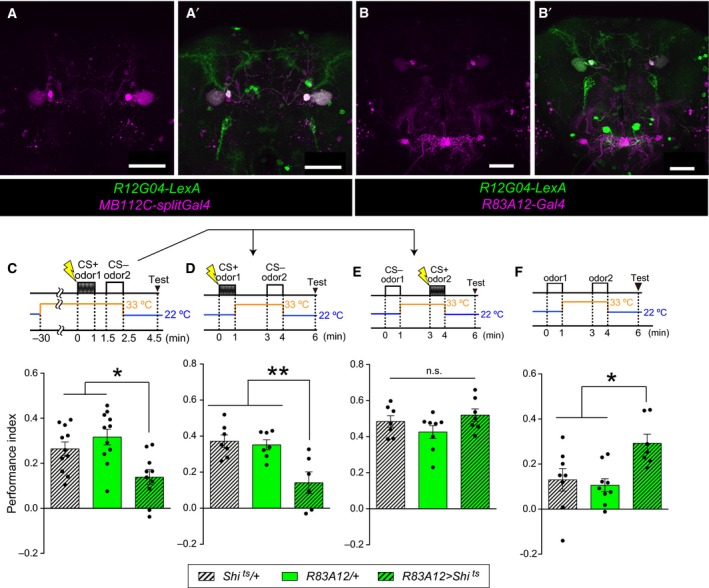
R83A12 driver also induced STM acquisition impairment and BGAM formation. (A, A’) MB112C‐splitGal4 and R12G04‐LexA expressed mCD8::RFP and mCD8::GFP, respectively. Both drivers label MBON‐γ1pedc. Scale bars: 50 μm. (B, B’) R83A12‐Gal4 and R12G04‐LexA expressed mCD8::RFP and mCD8::GFP, respectively. Both drivers label MBON‐γ1pedc. Scale bars: 50 μm. (C) Blocking synaptic outputs from R83A12‐positive neurons at the training stage impaired STM (ANOVA, n = 11, 11, 10). The flies were preheated at 33 °C before training for 30 min at 33 °C. Immediately after the training, the flies were transferred to 22 °C and tested at 22 °C. (D) Blocking synaptic outputs from R83A12‐positive neurons during the CS‐ presentation impaired STM (ANOVA, n = 7, 7, 6). (E) Blocking synaptic outputs from R83A12‐positive neurons during the CS+ presentation did not impair STM (ANOVA, n = 7, 8, 7). (F) Blocking synaptic outputs from R83A12‐positive neurons during odor presentation caused aversive STM, as compared to controls (ANOVA, n = 8, 9, 7). The Performance Index in this figure was calculated for odor 2, and the positive index indicates that flies avoid odor 2 over odor 1. (C–F) All bar graphs are mean ± SEM, and dots represent individual trials. *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, n.s.: P > 0.05.
