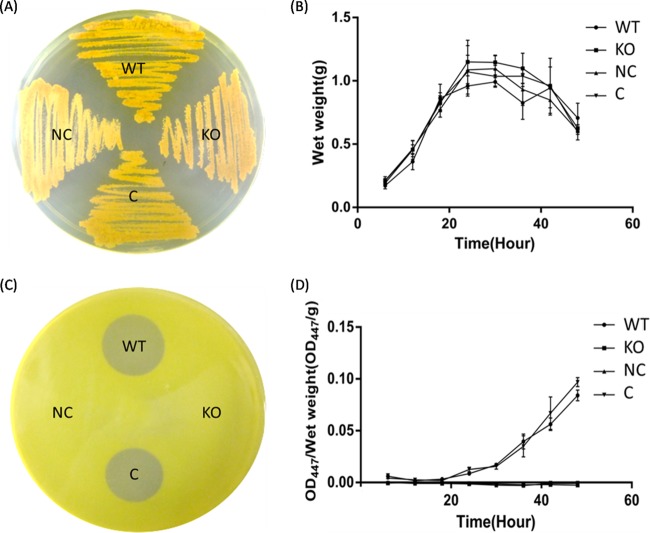
FIG 2.
RifZ stringently regulates rifamycin biosynthesis in A. mediterranei U32. (A) Growth of A. mediterranei strains on a Bennet plate. (B) Growth curves of different A. mediterranei strains. (C) Bacterial inhibition test of different A. mediterranei strains using Sarcina lutea as the indicator. (D) Rifamycin production by different A. mediterranei strains, detected by a chemical method. Both NC and KO strains lost the ability to produce rifamycin. WT, wild type; KO, rifZ knockout mutant; NC, KO strain integrated with pDZL803, a negative control; C, KO strain integrated with pDZL8031, a complementation strain.