Figure 1.
Directional RNAi Gene Enrichment Ranking (dRIGER) captures the consistency of differential effects of multiple shRNAs and transforms shRNA-level data into gene-level data.
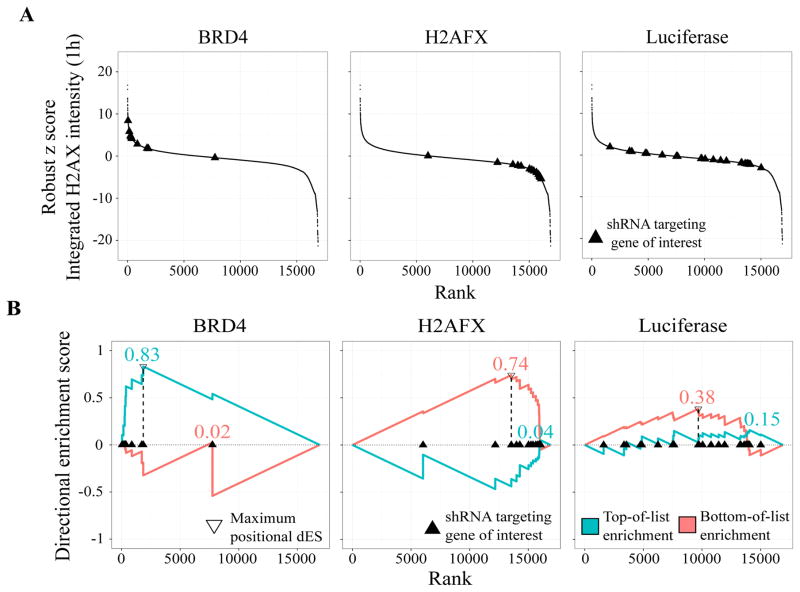
(A) S-curves of shRNAs targeting the genes Brd4, H2AFX, and the negative control luciferase, for integrated γH2AX intensity 1h after IR. As expected, knock-down with most shRNAs targeting the chromatin modifier Brd4 leads to vastly increased γH2AX intensity while most shRNAs targeting H2AFX have the opposite knock-down effect. shRNAs targeting the negative control luciferase surprisingly induce a wide variety of different phenotypic responses, including increased and decreased γH2AX intensities.
(B) Directional ES (dES) of Brd4, H2AFX, and the negative control luciferase for integrated γH2AX intensity 1h after IR. dRIGER rewards strong, consistent knock-down phenotypes with high dES. shRNAs targeting Brd4 and H2AFX are enriched at the top and bottom of the rank-ordered list of all screened shRNA respectively, resulting in high dES. shRNAs targeting luciferase are widely spread over the entire list, resulting in a substantially lower dES.