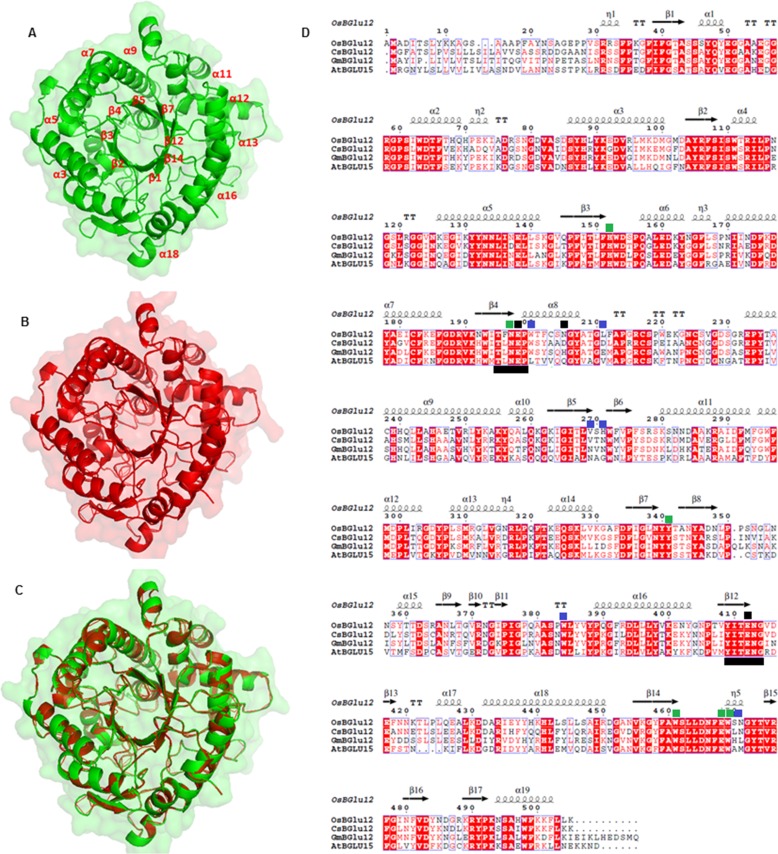
FIGURE 1.
Structural analysis of CsBGlu12. A, homology model of CsBGlu12 carried out by SWISS-MODEL software depicting characteristic (β/α)8 TIM barrel- shaped structure; B, rice Os4BGlu12 (3ptk) used as template; and C, superimposed structure of CsBGlu12 and Os4BGlu12. D, multiple sequence alignment carried out by ClustalW and analyzed by ESPript 3 software. The alignment shows secondary structure elements of the (α/β)8 barrel structure, containing the two catalytic glutamates (black squares), highly conserved residues involved in glucose binding (green squares) and residues involved in aglycone binding (blue squares). Conserved peptide motifs Thr-(Phe/Leu)-Asn-Glu-Pro (T(F/L)NEP) and Tyr-Ile-Thr-Glu-Asn-Gly (YITENG) are underlined in black. Red boxes denote the sites of perfect sequence identity. The protein sequences used in this study include C. sativus CsBGlu12 (KX790358), A. thaliana AtBGlu15 (O64879.1), O. sativa Os4BGlu12 (Q7XKV4.2), and Glycine max GmBGlu12 (XP_006590951).