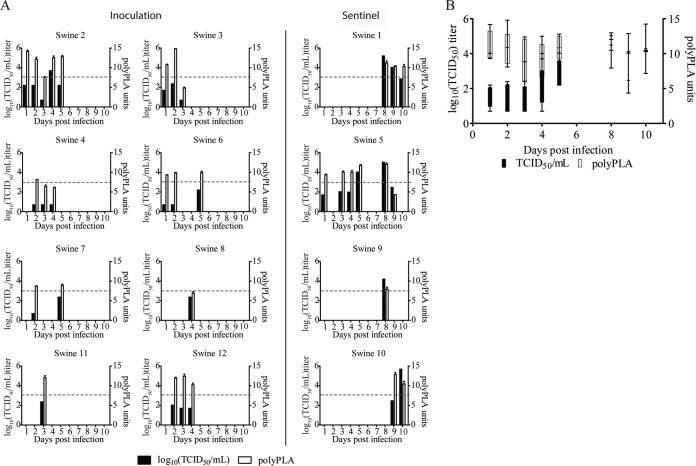
FIG 2.
Comparison of sensitivity of cell culture-based viral titration and polyclonal serum-based proximity ligation assay (polyPLA) in detecting influenza A viruses (IAVs) in nasal wash and nasal swab samples collected from feral swine infected with A/swine/Texas/A01104013/2012(H3N2). (A) Variations of TCID50 and polyPLA titers in 12 swine. The horizontal dashed line indicates 1,000 TCID50/ml. (B) Average number of days after virus challenge that virus could be detected by TCID50 and polyPLA. The whiskers of the box-and-whisker plots denote the smaller value to the larger value, while the box extends to the 25th and 75th percentiles, with the median in the middle. The infecting virus belongs to swine influenza A virus (IAV) antigenic cluster H3N2 swine IAV-ß. Swine 1 to 8 were inoculated nasally with virus; swine 9 to 12 were sentinel swine housed in the same room. Among a total of 120 samples collected from these 12 swine, 42 samples with detectable TCID50 were used in this study (see Table S1 in the supplemental material) (29).