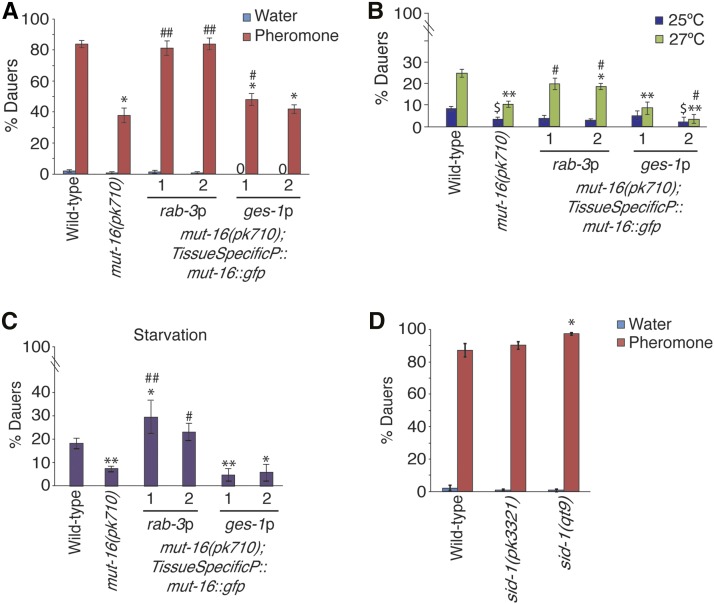
Figure 3.
MUT-16 is required in neurons for dauer formation. (A) Proportion of animals forming dauers in response to high pheromone and water plates is shown for pan-neuronal (rab-3p) and intestinal (ges-1p) mut-16 rescue strains. * P < 0.0005 compared to wild-type on pheromone plates; # P < 0.05 and ## P < 0.0005 compared to mut-16(pk710), respectively, on pheromone plates; one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test. N ≥ 3 trials; n ≥ 213 animals. (B) Proportion of animals forming dauers in response to 25 and 27° is shown for pan-neuronal and intestinal mut-16 rescue strains. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.0005 compared to wild-type at 27°; # P < 0.005 compared to mut-16(pk710) at 27°; $ P < 0.05 compared to wild-type at 25°; one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test. N = 3 trials; n ≥ 119 animals. (C) Proportion of animals forming dauers in response to starvation conditions for pan-neuronal and intestinal mut-16 rescue strains. * P < 0.05 and ** P < 0.005 compared to wild-type; # P < 0.005 and ## P < 0.0005 compared to mut-16(pk710); one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test. N = 3 trials; n ≥ 196 animals. (D) Proportion of sid-1 animals forming dauers in response to pheromone. * P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with LSD post hoc test. N = 3 trials; n ≥ 480 animals. All error bars represent SEM.