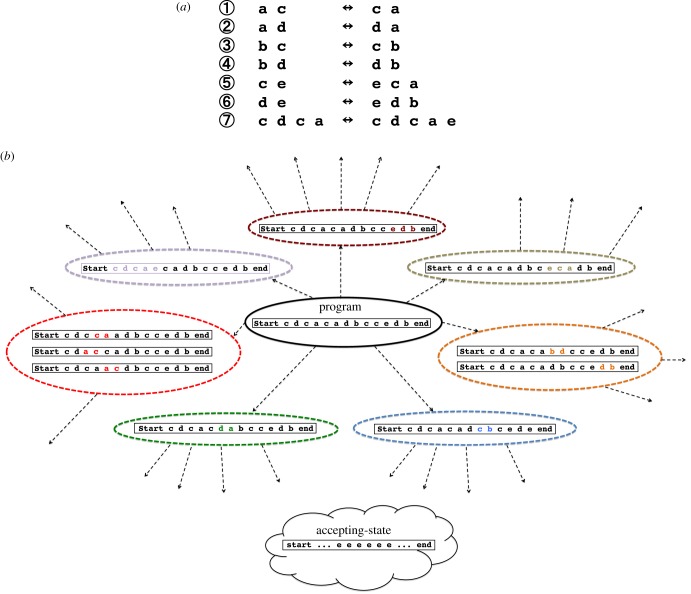
Figure 2.
A universal Thue system. (a) A set of universal Thue rules: rules 1–4 require symbol transposition; rule 7 requires symbol insertion (forward) and deletion (reverse); and rules 5 and 6 require transposition, insertion (forward) and deletion (reverse). (b) Part of trace of the execution of the universal Thue system (an NUTM): the tree of all its possible computations. The root of the tree is the initial program. The child nodes of the root are the subsequent Thue sequences generated from the initial program by application of one of the seven Thue rules: note that the antecedent of a rule (e.g. ca—the reverse of rule 1) may occur multiple times. Thue rules are recursively applied until the accepting state is produced, thus execution of a program generates a potentially exponential number of states in P time.