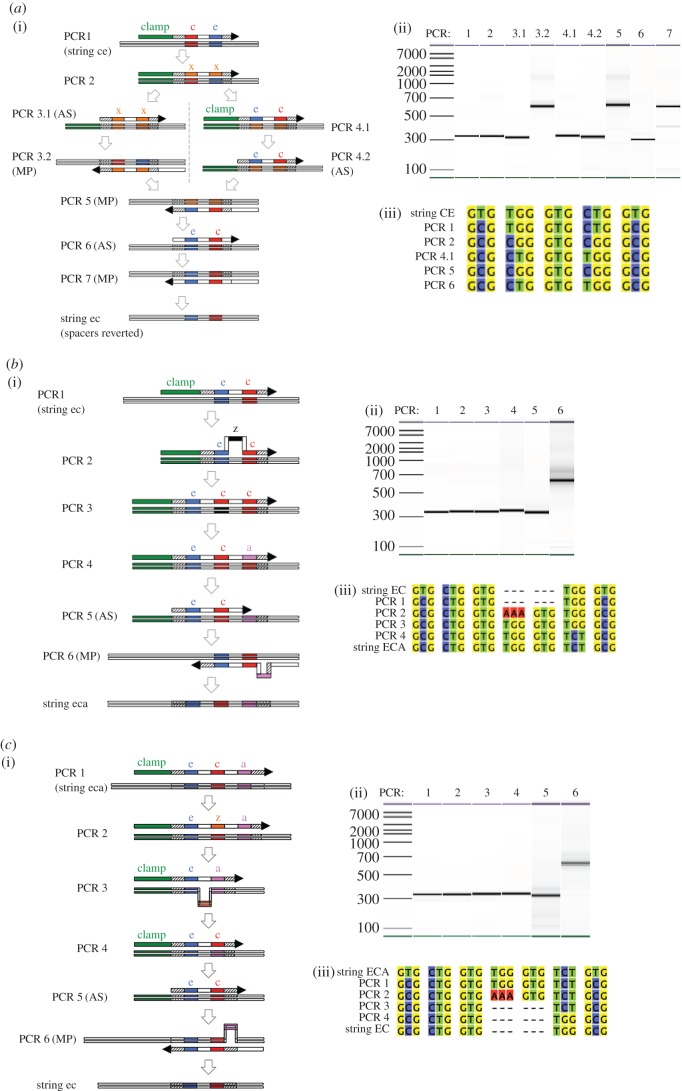
Figure 6.
Thue rule implementation. (a) Microprogram for swapping ce → ec. (i) The clamp sequence is first inserted and the outer s symbols changed to s' (PCR1). This clamp and spacer sequence is then bound by the primer in PCR2, which replaces the ce symbols with an xx sequence. Asymmetric PCR (AS) is then used to remove the clamp and create a megaprimer, which is used to replace ce with xx in the string (megaprimer PCR annotated ‘MP’, PCR 3.1 and 3.2). In parallel, the xx symbols are changed to ec by symmetric PCR (PCR 4.1), and then a megaprimer produced removing the clamp (PCR 4.2). This megaprimer is then employed to replace the sequence xx with ec in the string (PCR 5). Finally, the s' symbols are returned to s to complete the microprogram (PCR 6 and 7). (ii) Capillary electrophoresis analysis of the PCR products from each PCR step. (iii) Sequence alignment of DNA sequencing of the key steps in the microprogram. (b) Microprogram for the insertion ec → eca. (i) Following the recognition of ec the clamp is inserted and outer spacers changed (s to s', PCR 1). A non-coding symbol z is then inserted, which exploits the strong binding for the existing e and c with the modified s' spacers (PCR 2), which promotes a loop to occur during DNA hybridization. This symbol is then edited to c (PCR 3), and the other c changed to a (PCR 4). Asymmetric PCR is then used to generate a megaprimer for the eca sequence (PCR 5), which is then used to insert this new sequence into the tape (PCR 6). (ii) Capillary electrophoresis analysis of the PCR products from each PCR step. (iii) Sequence alignment of DNA sequencing of the key steps in the microprogram. (c) Microprogram for the deletion eca → ec. (i) The clamp and altered spacers s' are inserted upon recognition of eca in PCR 1. The middle symbol (c) is edited to a non-coding z (PCR 2) before deletion of this symbol by recognition of ea in the subsequent step (PCR 3). As with the insertion microprogram, the strength of DNA hybridization between the clamp, s'e and as' promotes the PCR primer to loop over the z symbol to delete it. Following deletion the symbol sequence ec is created (PCR 4), and the clamp removed by asymmetric PCR (PCR 5). Finally, the megaprimer is used to delete the original symbol a from the string. (ii) Capillary electrophoresis analysis of the PCR products from the deletion microprogram. (iii) Alignment of sequencing data from the key PCR steps.