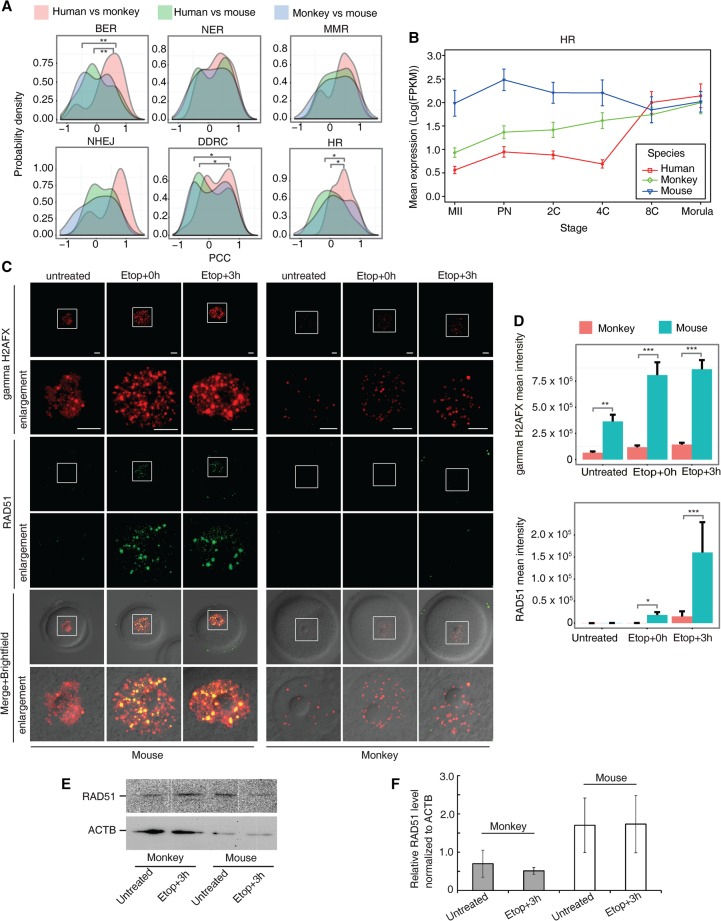
Figure 5.
Comparison of six groups of DDR and HR-mediated repair genes among three species. (A) Distribution of pair-wise PCC. Genes in the BER, DDRC, and HR groups were statistically different between the primates and mouse (P-value <0.05, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). (B) Mean log-transformed expression pattern of HR-related genes (EME1/Eme1, RAD51/Rad51, RAD54L/Rad54l, RECQL/Recql, SHFM1/Shfm1, UBA2/Uba2, and XRCC2/Xrcc2) in human, monkey, and mouse. (C) Examination of gamma H2AFX and RAD51 foci in untreated and etoposide-treated GV oocytes recovered for 0 h (Etop+0h) and 3 hr (Etop+3h). More gamma H2AFX foci were observed in mouse GV oocytes than in monkey GV oocytes after etoposide treatment. Consistently, more mouse oocytes accumulated RAD51 on damage sites, whereas fewer monkey oocytes had RAD51 foci formation. Images in squares are enlarged in the enlargement panels. (D) Quantification of fluorescence foci intensity of gamma H2AFX (top) and RAD51 (bottom). Intensity was normalized by the number of oocytes examined. (E) Immunoblotting analysis of RAD51 and ACTB protein level in mouse and monkey GV oocytes untreated or treated with etoposide followed by 3-h recovery. (F) Quantification of RAD51 protein level by normalization to ACTB. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. Scale bar, 10 μm. (*) P-value <0.05, (**) P-value <0.001, (***) P-value <0.0001, two-tailed t-test. (A,B) Based on monkey individual-oocyte/embryo sequencing data. Similar results for the pooled-embryo data are shown in Supplemental Figure S14.